Generation and Characterization of a Human/Mouse Chimeric GD2-Mimicking Anti-Idiotype Antibody Ganglidiximab for Active Immunotherapy against Neuroblastoma
- PMID: 26967324
- PMCID: PMC4788445
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150479
Generation and Characterization of a Human/Mouse Chimeric GD2-Mimicking Anti-Idiotype Antibody Ganglidiximab for Active Immunotherapy against Neuroblastoma
Abstract
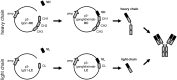
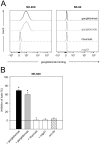
Vaccination with proteins mimicking GD2 that is highly expressed on neuroblastoma (NB) cells is a promising strategy in treatment of NB, a pediatric malignancy with poor prognosis. We previously showed efficacy of ganglidiomab in vivo, a murine anti-idiotype (anti-Id) IgG1. In order to tailor immune responses to variable regions, we generated a new human/mouse chimeric anti-Id antibody (Ab) ganglidiximab by replacing murine constant fragments with corresponding human IgG1 regions. DNA sequences encoding for variable regions of heavy (VH) and light chains (VL) were synthesized by RT-PCR from total RNA of ganglidiomab-producing hybridoma cells and further ligated into mammalian expression plasmids with coding sequences for constant regions of human IgG1 heavy and light chains, respectively. We established a stable production cell line using Chinese hamster ovarian (CHO) cells co-transfected with two expression plasmids driving the expression of either ganglidiximab heavy or light chain. After purification from supernatants, anti-idiotypic characteristics of ganglidiximab were demonstrated. Binding of ganglidiximab to anti-GD2 Abs of the 14.18 family as well as to NK-92tr cells expressing a GD2-specific chimeric antigen receptor (scFv(ch14.18)-zeta) was shown using standard ELISA and flow cytometry analysis, respectively. Ganglidiximab binding affinities to anti-GD2 Abs were further determined by surface plasmon resonance technique. Moreover, binding of anti-GD2 Abs to the nominal antigen GD2 as well as GD2-specific Ab-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC, CDC) was competitively inhibited by ganglidiximab. Finally, ganglidiximab was successfully used as a protein vaccine in vivo to induce a GD2-specific humoral immune response. In summary, we report generation and characterization of a new human/mouse chimeric anti-Id Ab ganglidiximab for active immunotherapy against NB. This Ab may be useful to tailor immune responses to the paratope regions mimicking GD2 overexpressed in NB.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Validated detection of anti-GD2 antibody ch14.18/CHO in serum of neuroblastoma patients using anti-idiotype antibody ganglidiomab.J Immunol Methods. 2013 Dec 15;398-399:51-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2013.09.008. Epub 2013 Sep 18. J Immunol Methods. 2013. PMID: 24055592
-
Vaccination with anti-idiotype antibody ganglidiomab mediates a GD(2)-specific anti-neuroblastoma immune response.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013 Jun;62(6):999-1010. doi: 10.1007/s00262-013-1413-y. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23591980 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-neuroblastoma effect of ch14.18 antibody produced in CHO cells is mediated by NK-cells in mice.Mol Immunol. 2005 Jul;42(11):1311-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2004.12.018. Epub 2005 Apr 7. Mol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15950727
-
Targeted immunotherapy for high-risk neuroblastoma--the role of monoclonal antibodies.Ann Pharmacother. 2013 Feb;47(2):210-8. doi: 10.1345/aph.1R353. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Ann Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 23386066 Review.
-
Anti-GD2 immunotherapy for neuroblastoma.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2017 Oct;17(10):889-904. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2017.1364995. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 28780888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GM-CSF, G-CSF or no cytokine therapy with anti-GD2 immunotherapy for high-risk neuroblastoma.Int J Cancer. 2024 Apr 15;154(8):1340-1364. doi: 10.1002/ijc.34815. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Int J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38108214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Response and Outcome of High-Risk Neuroblastoma Patients Immunized with Anti-Idiotypic Antibody Ganglidiomab: Results from Compassionate-Use Treatments.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 25;14(23):5802. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235802. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497290 Free PMC article.
-
GD2-targeting therapy: a comparative analysis of approaches and promising directions.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 15;15:1371345. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1371345. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38558810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Mimicry of the Dengue Virus Envelope Glycoprotein Revealed by the Crystallographic Study of an Idiotype-Anti-idiotype Fab Complex.J Virol. 2017 Aug 10;91(17):e00406-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00406-17. Print 2017 Sep 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28637753 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Anti-GD2 Immunotherapy for Treatment of High-risk Neuroblastoma.J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2019 Apr;41(3):163-169. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000001369. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30897608 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alice L.Yu. Progress in Treatment of High-risk Neuroblastoma with Immunotherapy. American Society of Clinical Oncology, American Society of Clinical Oncology.
-
- Maris JM, Hogarty MD, Bagatell R, Cohn SL. Neuroblastoma. Lancet. 2007. June 23;369(9579):2106–20. - PubMed
-
- Matthay KK, Reynolds CP, Seeger RC, Shimada H, Adkins ES, Haas-Kogan D, et al. Long-term results for children with high-risk neuroblastoma treated on a randomized trial of myeloablative therapy followed by 13-cis-retinoic acid: a children's oncology group study. J Clin Oncol. 2009. March 1;27(7):1007–13. 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.8925 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheung NK, Neely JE, Landmeier B, Nelson D, Miraldi F. Targeting of ganglioside GD2 monoclonal antibody to neuroblastoma. J Nucl Med. 1987. October;28(10):1577–83. - PubMed
-
- Schulz G, Cheresh DA, Varki NM, Yu A, Staffileno LK, Reisfeld RA. Detection of ganglioside GD2 in tumor tissues and sera of neuroblastoma patients. Cancer Res. 1984. December;44(12 Pt 1):5914–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

