Multitargeting activity of miR-24 inhibits long-term melatonin anticancer effects
- PMID: 26967561
- PMCID: PMC4991473
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7978
Multitargeting activity of miR-24 inhibits long-term melatonin anticancer effects
Abstract
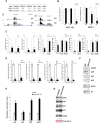
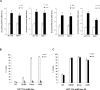
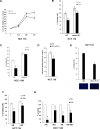
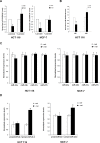
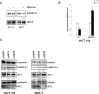
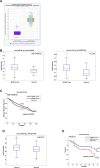
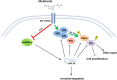
We have previously shown that melatonin exerts tumor suppressor activities by inducing the p38-p53 axis. This occurred within a few hours while no data are available on how melatonin pathway can be sustained on the long term. Here we show that miR-24, which has been demonstrated to target genes involved in the DNA repair process, targets p38, p53, PML and H2AX simultaneously. We show that long-term treatment with melatonin can decrease miR-24 levels post-transcriptionally, which pairs with a long-wave regulation of genes involved in cell proliferation, DNA damage, RNA metabolism and cell shape and transformation. Moreover, we show that melatonin can inhibit cell proliferation and migration, at least in part, by downregulating miR-24. Furthermore, we propose the involvement of hnRNP A1, which is downregulated by melatonin and involved in miRNA processing, in the regulation of miR-24 levels by melatonin. We conclude showing that miR-24 is upregulated in colon, breast and head and neck datasets and its levels negatively correlate with overall survival.
Keywords: PML; RNA-Seq; melatonin; miR-24; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aoki H, Ozeki Y, Yamada N. Hypersensitivity of melatonin suppression in response to light in patients with delayed sleep phase syndrome. Chronobiology international. 2001;18:263–271. - PubMed
-
- Carbajo-Pescador S, Garcia-Palomo A, Martin-Renedo J, Piva M, Gonzalez-Gallego J, Mauriz JL. Melatonin modulation of intracellular signaling pathways in hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cell line: role of the MT1 receptor. Journal of pineal research. 2011;51:463–471. - PubMed
-
- Cuesta S, Kireev R, Forman K, Garcia C, Escames G, Ariznavarreta C, Vara E, Tresguerres JA. Melatonin improves inflammation processes in liver of senescence-accelerated prone male mice (SAMP8) Experimental gerontology. 2010;45:950–956. - PubMed
-
- Jones CR, Campbell SS, Zone SE, Cooper F, DeSano A, Murphy PJ, Jones B, Czajkowski L, Ptacek LJ. Familial advanced sleep-phase syndrome: A short-period circadian rhythm variant in humans. Nature medicine. 1999;5:1062–1065. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

