The interleukin-20 receptor axis in early rheumatoid arthritis: novel links between disease-associated autoantibodies and radiographic progression
- PMID: 26968800
- PMCID: PMC4788924
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-0964-7
The interleukin-20 receptor axis in early rheumatoid arthritis: novel links between disease-associated autoantibodies and radiographic progression
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is often characterized by the presence of rheumatoid factor, anti-citrullinated protein antibodies, and bone erosions. Current therapies can compromise immunity, leading to risk of infection. The interleukin-20 receptor (IL-20R) axis comprising IL-19, IL-20, and IL-24 and their shared receptors activates tissue homeostasis processes but not the immune system. Consequently, modulation of the IL-20R axis may not lead to immunosuppression, making it an interesting drug target. We evaluated the role of the IL-20R axis in RA and associations between plasma cytokine levels and clinical disease.
Methods: Plasma IL-19, IL-20, and IL-24 levels were measured in early RA patients during a treat-to-target strategy by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. The IL-20R1 and IL-22R1 levels in paired peripheral blood mononuclear cells and synovial fluid mononuclear cells from a different cohort of RA patients were evaluated by flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. Monocytes/macrophages were stimulated with heat-aggregated human immunoglobulin immune complexes and immune complexes containing citrullinated fibrinogen, and osteoclasts were incubated with IL-19, IL-20, and IL-24.
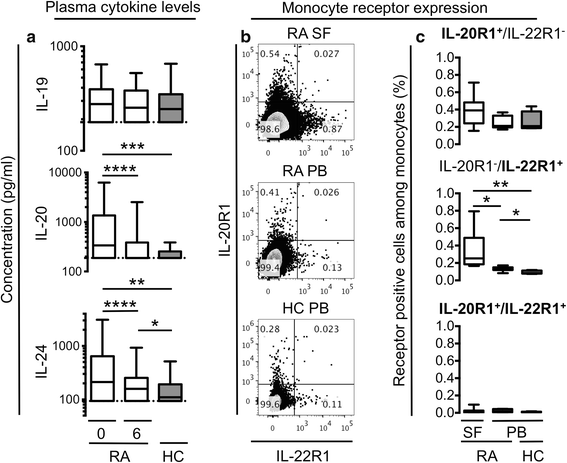
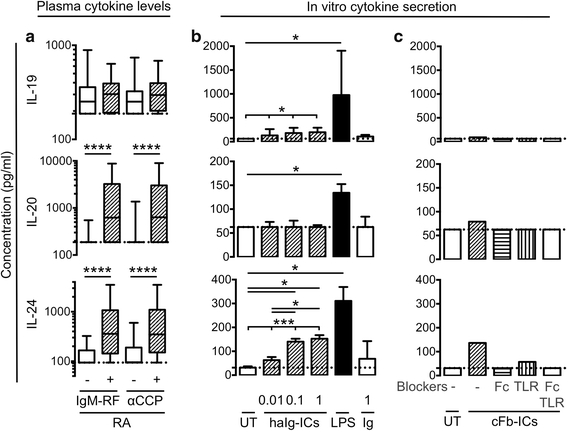
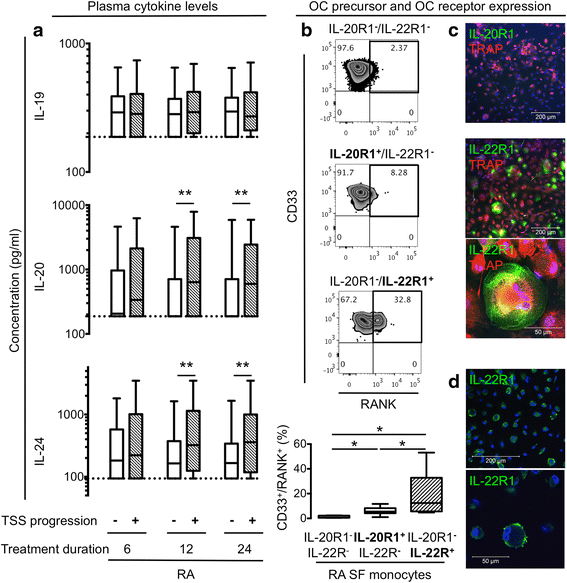
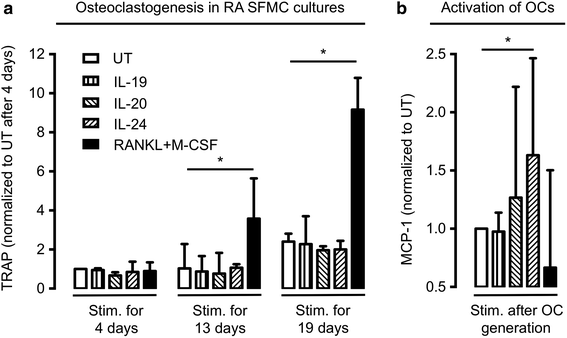
Results: The plasma concentrations of IL-20 and IL-24 (but not IL-19) were increased in early RA patients compared with healthy controls (both P < 0.002) and decreased after 6 months of treatment (both P < 0.0001). The expression of IL-22R1 (but not IL-20R1) was increased on monocytes from RA synovial fluid compared with monocytes from both RA and healthy control peripheral blood. The plasma concentrations of IL-20 and IL-24 were increased in rheumatoid factor and anti-citrullinated protein antibody positive compared with negative early RA patients (all P < 0.0001). Immune complexes stimulated the production of the IL-20R cytokines by monocytes/macrophages. Increased baseline plasma concentrations of IL-20 and IL-24 were associated with Sharp-van der Heijde score progression after 24 months (Spearman's rho = 0.19 and 0.26, both P < 0.05) in the early RA patients. The IL-22R1 was expressed by osteoclast precursors and in multinucleated osteoclasts. IL-20 and IL-24 increased the secretion of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 by these cells.
Conclusions: This study suggests that IL-20 and IL-24 link RA-associated autoantibodies with radiographic progression via the IL-22R1. Modulation of this axis holds promise as feasible anti-erosive treatment modalities in seropositive RA.
Keywords: Autoantibody(ies); Bone resorption; Cytokines; Monocytes/macrophages; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A regulatory effect of IL-21 on T follicular helper-like cell and B cell in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 Nov 23;14(6):R255. doi: 10.1186/ar4100. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 23176102 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble OX40L is associated with presence of autoantibodies in early rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Oct 30;16(5):474. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0474-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25359291 Free PMC article.
-
IgA Immune Complexes Induce Osteoclast-Mediated Bone Resorption.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 1;12:651049. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.651049. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34276648 Free PMC article.
-
The IL-20 Cytokine Family in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Spondyloarthritis.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 25;9:2226. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02226. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30319661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autoantibody-mediated bone loss.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2014 Mar;12(1):17-21. doi: 10.1007/s11914-013-0185-9. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2014. PMID: 24407713 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased interleukin (IL)-20 and IL-24 target osteoblasts and synovial monocytes in spondyloarthritis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 Sep;189(3):342-351. doi: 10.1111/cei.12973. Epub 2017 May 2. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28369789 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-18, interleukin-20, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-1, MMP-3) as markers of psoriatic arthritis disease severity and their correlations with biomarkers of inflammation and turnover of joint cartilage.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2020 Dec;37(6):1001-1008. doi: 10.5114/ada.2020.94903. Epub 2020 May 4. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2020. PMID: 33603622 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol displays anti-inflammatory properties in an ex vivo model of immune mediated inflammatory arthritis.BMC Rheumatol. 2018 Oct 10;2:27. doi: 10.1186/s41927-018-0036-5. eCollection 2018. BMC Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 30886977 Free PMC article.
-
Responses to Cytokine Inhibitors Associated with Cellular Composition in Models of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Arthritis.ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020 Jan;2(1):3-10. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11094. Epub 2019 Nov 11. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31943973 Free PMC article.
-
IL-20 bone diseases involvement and therapeutic target potential.J Biomed Sci. 2018 Apr 24;25(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12929-018-0439-z. J Biomed Sci. 2018. PMID: 29690863 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

