Rapid atrial pacing induces myocardial fibrosis by down-regulating Smad7 via microRNA-21 in rabbit
- PMID: 26968995
- PMCID: PMC5043001
- DOI: 10.1007/s00380-016-0808-z
Rapid atrial pacing induces myocardial fibrosis by down-regulating Smad7 via microRNA-21 in rabbit
Abstract
Tachycardia-induced atrial fibrosis is a hallmark of the structural remodeling of atrial fibrillation (AF). The mechanisms underlying tachycardia-induced atrial fibrosis remain unclear. In our previous study, we found that Smad7-downregulation promoted the development of atrial fibrosis in AF. Fibroblasts are enriched in microRNA-21 (miR-21), which contributes to the development of fibrosis and heart failure in the cardiovascular system. Our study was designed to test the hypothesis that miR-21 reinforces the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway in AF-induced atrial fibrosis by down-regulating Smad7. Rapid atrial pacing (RAP, 1000 ppm) was applied to the left atrium of the rabbit heart to induce atrial fibrillation and fibrosis. qRT-PCR and northern blot analysis revealed that RAP caused a marked increase in the expression of miR-21. Transfection with a miR-21 inhibitor significantly increased the expression of Smad7, while the expression of collagen I/III significantly decreased. These changes were implicated in the AF-induced release of miR-21 and down-regulation of Smad7. Adult rat cardiac fibroblasts treated with TGF-β1 showed increased miR-21 expression and decreased Smad7 expression. Pretreatment with a TGF-β1 inhibitor reduced the TGF-β1-induced up-regulation of miR-21. Pretreatment with pre-miR-21 and a miR-21 inhibitor significantly decreased and increased Smad7 expression, respectively. This result was negatively correlated with the expression of collagen I/III in fibroblasts. Moreover, the results of a luciferase activity assay suggest that Smad7 is a validated miR-21 target in CFs. Our results provide compelling evidence that the miR-21 specific degradation of Smad7 may decrease the inhibitory feedback regulation of TGF-β1/Smad signaling and serves as a new insight of the mechanism of atrial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Atrial fibrosis; MicroRNA-21; Smad7; Transforming growth factor-β1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
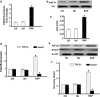


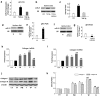

References
-
- Matsuda H, Parwani AS, Attanasio P, Huemer M, Wutzler A, Blaschke F, Haverkamp W, Boldt LH. Atrial rhythm influences catheter tissue contact during radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: comparison of contact force between sinus rhythm and atrial fibrillation. Heart Vessels. 2015 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoshiyama T, Yamabe H, Koyama J, Kanazawa H, Ogawa H. Left atrial electrophysiologic feature specific for the genesis of complex fractionated atrial electrogram during atrial fibrillation. Heart Vessels. 2015 - PubMed
-
- Aldhoon B, Melenovsky V, Peichl P, Kautzner J. New insights into mechanisms of atrial fibrillation. Physiol Res. 2010;59:1–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

