Clonal expansion of CD4(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with IgG4-related disease
- PMID: 26971690
- PMCID: PMC5014627
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.12.1330
Clonal expansion of CD4(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with IgG4-related disease
Abstract
Background: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic condition of unknown cause characterized by highly fibrotic lesions with dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates. CD4(+) T cells constitute the major inflammatory cell population in IgG4-RD lesions.
Objective: We used an unbiased approach to characterize CD4(+) T-cell subsets in patients with IgG4-RD based on their clonal expansion and ability to infiltrate affected tissue sites.
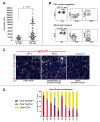
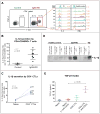
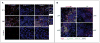
Methods: We used flow cytometry to identify CD4(+) effector/memory T cells in a cohort of 101 patients with IgG4-RD. These expanded cells were characterized by means of gene expression analysis and flow cytometry. Next-generation sequencing of the T-cell receptor β chain gene was performed on CD4(+)SLAMF7(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and CD4(+)GATA3(+) TH2 cells in a subset of patients to identify their clonality. Tissue infiltration by specific T cells was examined by using quantitative multicolor imaging.
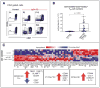
Results: CD4(+) effector/memory T cells with a cytolytic phenotype were expanded in patients with IgG4-RD. Next-generation sequencing revealed prominent clonal expansions of these CD4(+) CTLs but not CD4(+)GATA3(+) memory TH2 cells in patients with IgG4-RD. The dominant T cells infiltrating a range of inflamed IgG4-RD tissue sites were clonally expanded CD4(+) CTLs that expressed SLAMF7, granzyme A, IL-1β, and TGF-β1. Clinical remission induced by rituximab-mediated B-cell depletion was associated with a reduction in numbers of disease-associated CD4(+) CTLs.
Conclusions: IgG4-RD is prominently linked to clonally expanded IL-1β- and TGF-β1-secreting CD4(+) CTLs in both peripheral blood and inflammatory tissue lesions. These active, terminally differentiated, cytokine-secreting effector CD4(+) T cells are now linked to a human disease characterized by chronic inflammation and fibrosis.
Keywords: CD4(+) cytotoxic T cells; Fibrosis; IL-1β; IgG(4); IgG(4)-related disease; T(H)2 cells; rituximab.
Copyright © 2016 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no relevant conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:539–51. - PubMed
-
- Mahajan VS, Mattoo H, Deshpande V, Pillai SS, Stone JH. IgG4-Related Disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2014;9:315–47. - PubMed
-
- Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Lancet. 2015;385:1460–71. - PubMed
-
- Bruhns P, Iannascoli B, England P, Mancardi DA, Fernandez N, Jorieux S, et al. Specificity and affinity of human Fcgamma receptors and their polymorphic variants for human IgG subclasses. Blood. 2009;113:3716–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

