Remote Limb Preconditioning Generates a Neuroprotective Effect by Modulating the Extrinsic Apoptotic Pathway and TRAIL-Receptors Expression
- PMID: 26971954
- PMCID: PMC11482232
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-016-0360-5
Remote Limb Preconditioning Generates a Neuroprotective Effect by Modulating the Extrinsic Apoptotic Pathway and TRAIL-Receptors Expression
Abstract
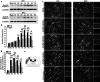
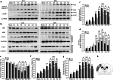
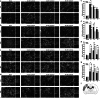
As remote limb preconditioning (RPC) ameliorates brain damage after ischemic cerebral stroke (ICS), the purpose of the present study was to explore the molecular mechanisms in the course of RPC. Results of TUNEL staining and cleaved caspase-3 expression showed that ischemia-induced neuronal apoptosis was inhibited by RPC. The expression changes in cleaved caspase-8, cFLIP, Bid itself, and its truncated form represented that RPC suppressed the activation of extrinsic apoptotic pathway during ICS. Then, the level of cytoplasmic cytochrome c was also decreased by RPC. In addition, RPC might partially suppress TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced extrinsic apoptosis through downregulation of TRAIL death receptors and upregulation of TRAIL decoy receptors. As a counterproof, immunoneutralization of TRAIL in dMCAO rats resulted in significant restraint of tissue damage and in a marked functional recovery. Our data complemented the knowledge of RPC neuroprotective mechanism and provided new evidence for its clinical application.
Keywords: Ischemic cerebral stoke; Neuronal apoptosis; Remote limb preconditioning; TRAIL-receptors.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Ischemic tolerance modulates TRAIL expression and its receptors and generates a neuroprotected phenotype.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jul 17;5(7):e1331. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.286. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25032854 Free PMC article.
-
Remote limb preconditioning protects against ischemia-induced neuronal death through ameliorating neuronal oxidative DNA damage and parthanatos.J Neurol Sci. 2016 Jul 15;366:8-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2016.04.038. Epub 2016 Apr 20. J Neurol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27288768
-
Ischemic Preconditioning Upregulates Decoy Receptors to Protect SH-SY5Y Cells from OGD Induced Cellular Damage by Inhibiting TRAIL Pathway and Agitating PI3K/Akt Pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Sep;57(9):3658-3670. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-01978-3. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32564286
-
A critical review of mechanisms regulating remote preconditioning-induced brain protection.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015 Nov 15;119(10):1135-42. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00169.2015. Epub 2015 May 7. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015. PMID: 25953834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinases as modulators of TRAIL-mediated extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway.BMB Rep. 2019 Feb;52(2):119-126. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.2.011. BMB Rep. 2019. PMID: 30638181 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning attenuates intestinal mucosal damage: insight from a rat model of ischemia-reperfusion injury.J Transl Med. 2019 Apr 29;17(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1885-4. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31036020 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke: The Basis of Current Therapies and Opportunity for New Ones.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 4;14(3):305. doi: 10.3390/biom14030305. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in intervention methods and brain protection mechanisms of in situ and remote ischemic postconditioning.Metab Brain Dis. 2021 Jan;36(1):53-65. doi: 10.1007/s11011-020-00562-x. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Metab Brain Dis. 2021. PMID: 33044640 Review.
-
MicroRNA-125a-3p is involved in early behavioral disorders in stroke-afflicted rats through the regulation of Cadm2.Int J Mol Med. 2017 Dec;40(6):1851-1859. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3179. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Int J Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 29039453 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic cell death in disease-Current understanding of the NCCD 2023.Cell Death Differ. 2023 May;30(5):1097-1154. doi: 10.1038/s41418-023-01153-w. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Cell Death Differ. 2023. PMID: 37100955 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aktas O, Smorodchenko A, Brocke S, Infante-Duarte C, Schulze Topphoff U, Vogt J, Prozorovski T, Meier S, Osmanova V, Pohl E, Bechmann I, Nitsch R, Zipp F (2005) Neuronal damage in autoimmune neuroinflammation mediated by the death ligand TRAIL. Neuron 46(3):421–432 - PubMed
-
- Bi Q, Song Z (2011) The effects of combination anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidation drugs in acute stroke. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 50(2):140–143 - PubMed
-
- Bin L, Li X, Xu LG, Shu HB (2002) The short splice form of Casper/c-FLIP is a major cellular inhibitor of TRAIL-induced apoptosis. FEBS Lett 510(1–2):37–40 - PubMed
-
- Cantarella G, Uberti D, Carsana T, Lombardo G, Bernardini R, Memo M (2003) Neutralization of TRAIL death pathway protects human neuronal cell line from beta-amyloid toxicity. Cell Death Differ 10(1):134–141 - PubMed
-
- Cantarella G, Lempereur L, D’alcamo MA, Risuglia N, Cardile V, Pennisi G, Scoto GM, Bernardini R, (2007) Trail interacts redundantly with nitric oxide in rat astrocytes: potential contribution to neurodegenerative processes. J Neuroimmunol 182(1–2):41–47 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

