Rutaecarpine ameliorates hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia in fat-fed, streptozotocin-treated rats via regulating the IRS-1/PI3K/Akt and AMPK/ACC2 signaling pathways
- PMID: 26972495
- PMCID: PMC4820804
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2015.167
Rutaecarpine ameliorates hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia in fat-fed, streptozotocin-treated rats via regulating the IRS-1/PI3K/Akt and AMPK/ACC2 signaling pathways
Abstract
Aim: We have shown that rutaecarpine extracted from the dried fruit of Chinese herb Evodia rutaecarpa (Juss) Benth (Wu Zhu Yu) promotes glucose consumption and anti-inflammatory cytokine expression in insulin-resistant primary skeletal muscle cells. In this study we investigated whether rutaecarpine ameliorated the obesity profiles, lipid abnormality, glucose metabolism and insulin resistance in rat model of hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia.
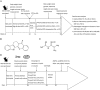
Methods: Rats fed on a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, followed by injection of streptozotocin (30 mg/kg, ip) to induce hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia. One week after streptozotocin injection, the fat-fed, streptozotocin-treated rats were orally treated with rutaecarpine (25 mg·kg(-1)·d(-1)) or a positive control drug metformin (250 mg·kg(-1)·d(-1)) for 7 weeks. The body weight, visceral fat, blood lipid profiles and glucose levels, insulin sensitivity were measured. Serum levels of inflammatory cytokines were analyzed. IRS-1 and Akt/PKB phosphorylation, PI3K and NF-κB protein levels in liver tissues were assessed; pathological changes of livers and pancreases were examined. Glucose uptake and AMPK/ACC2 phosphorylation were studied in cultured rat skeletal muscle cells in vitro.
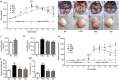
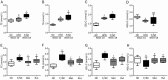
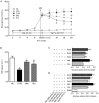
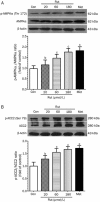
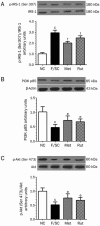
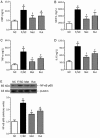
Results: Administration of rutaecarpine or metformin significantly decreased obesity, visceral fat accumulation, water consumption, and serum TC, TG and LDL-cholesterol levels in fat-fed, streptozotocin-treated rats. The two drugs also attenuated hyperglycemia and enhanced insulin sensitivity. Moreover, the two drugs significantly decreased NF-κB protein levels in liver tissues and plasma TNF-α, IL-6, CRP and MCP-1 levels, and ameliorated the pathological changes in livers and pancreases. In addition, the two drugs increased PI3K p85 subunit levels and Akt/PKB phosphorylation, but decreased IRS-1 phosphorylation in liver tissues. Treatment of cultured skeletal muscle cells with rutaecarpine (20-180 μmol/L) or metformin (20 μmol/L) promoted the phosphorylation of AMPK and ACC2, and increased glucose uptake.
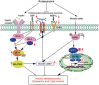
Conclusion: Rutaecarpine ameliorates hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia in fat-fed, streptozotocin-treated rats via regulating IRS-1/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in liver and AMPK/ACC2 signaling pathway in skeletal muscles.
Figures

References
-
- Fu J, Prasad HC. Changing epidemiology of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes in Chinese youth. Curr Diab Rep 2014; 14: 447. - PubMed
-
- Beagley J, Guariguata L, Weil C, Motala AA. Global estimates of undiagnosed diabetes in adults. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2014; 103: 150–60. - PubMed
-
- Kuivenhoven JA, Groen AK. Beyond the genetics of HDL: why is HDL cholesterol inversely related to cardiovascular disease? Handb Exp Pharmacol 2015; 224: 285–300. - PubMed
-
- Orme M, Fenici P, Lomon ID, Wygant G, Townsend R, Roudaut M. A systematic review and mixed-treatment comparison of dapagliflozin with existing anti-diabetes treatments for those with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled by sulfonylurea monotherapy. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2014; 6: 73. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

