Environmental Regulation of Yersinia Pathophysiology
- PMID: 26973818
- PMCID: PMC4773443
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00025
Environmental Regulation of Yersinia Pathophysiology
Abstract
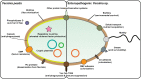
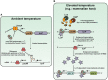
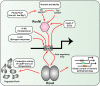
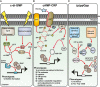
Hallmarks of Yersinia pathogenesis include the ability to form biofilms on surfaces, the ability to establish close contact with eukaryotic target cells and the ability to hijack eukaryotic cell signaling and take over control of strategic cellular processes. Many of these virulence traits are already well-described. However, of equal importance is knowledge of both confined and global regulatory networks that collaborate together to dictate spatial and temporal control of virulence gene expression. This review has the purpose to incorporate historical observations with new discoveries to provide molecular insight into how some of these regulatory mechanisms respond rapidly to environmental flux to govern tight control of virulence gene expression by pathogenic Yersinia.
Keywords: RovA; acidity; c-di-GMP; cAMP; extracytoplasmic stress; metabolism; temperature; transition metals.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNA Regulators: Formidable Modulators of Yersinia Virulence.Trends Microbiol. 2017 Jan;25(1):19-34. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2016.08.006. Epub 2016 Sep 17. Trends Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27651123 Review.
-
Coregulation of host-adapted metabolism and virulence by pathogenic yersiniae.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Oct 20;4:146. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00146. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25368845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic control of bacterial biofilms.J Appl Genet. 2016 May;57(2):225-38. doi: 10.1007/s13353-015-0309-2. Epub 2015 Aug 21. J Appl Genet. 2016. PMID: 26294280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Invasin and beyond: regulation of Yersinia virulence by RovA.Trends Microbiol. 2004 Jun;12(6):296-300. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.04.006. Trends Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15165608 Review.
-
Regulatory elements implicated in the environmental control of invasin expression in enteropathogenic Yersinia.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;603:156-66. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-72124-8_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17966412 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Genomics-Based Approaches for the Development of Intracellular Bacterial Pathogen Vaccines.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 31;15(1):152. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010152. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36678781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A global overview of the most important zoonotic bacteria pathogens transmitted from Rattus norvegicus to humans in urban environments.Infect Med (Beijing). 2022 Jul 30;1(3):192-207. doi: 10.1016/j.imj.2022.07.002. eCollection 2022 Sep. Infect Med (Beijing). 2022. PMID: 38077628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cyclic AMP Receptor Protein Regulates Quorum Sensing and Global Gene Expression in Yersinia pestis during Planktonic Growth and Growth in Biofilms.mBio. 2019 Nov 19;10(6):e02613-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02613-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31744922 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic relocalization of cytosolic type III secretion system components prevents premature protein secretion at low external pH.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 12;12(1):1625. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21863-4. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33712575 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of Survival after Vaccination in a Pneumonic Plague Model.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jan 19;10(2):145. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10020145. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214604 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

