Localized JNK signaling regulates organ size during development
- PMID: 26974344
- PMCID: PMC4848088
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.11491
Localized JNK signaling regulates organ size during development
Abstract
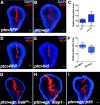
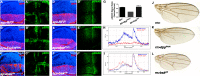
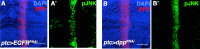
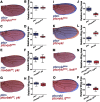
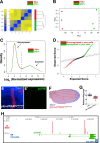
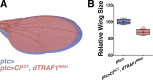
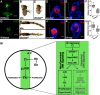
A fundamental question of biology is what determines organ size. Despite demonstrations that factors within organs determine their sizes, intrinsic size control mechanisms remain elusive. Here we show that Drosophila wing size is regulated by JNK signaling during development. JNK is active in a stripe along the center of developing wings, and modulating JNK signaling within this stripe changes organ size. This JNK stripe influences proliferation in a non-canonical, Jun-independent manner by inhibiting the Hippo pathway. Localized JNK activity is established by Hedgehog signaling, where Ci elevates dTRAF1 expression. As the dTRAF1 homolog, TRAF4, is amplified in numerous cancers, these findings provide a new mechanism for how the Hedgehog pathway could contribute to tumorigenesis, and, more importantly, provides a new strategy for cancer therapies. Finally, modulation of JNK signaling centers in developing antennae and legs changes their sizes, suggesting a more generalizable role for JNK signaling in developmental organ size control.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; Hedgehog; Hippo; JNK; TRAF4; development; developmental biology; size control; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impaired Hippo signaling promotes Rho1-JNK-dependent growth.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jan 27;112(4):1065-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1415020112. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25583514 Free PMC article.
-
The MAP kinase ERK and its scaffold protein MP1 interact with the chromatin regulator Corto during Drosophila wing tissue development.BMC Dev Biol. 2011 Mar 14;11:17. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-11-17. BMC Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21401930 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of flfl Triggers JNK-Dependent Cell Death in Drosophila.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:623573. doi: 10.1155/2015/623573. Epub 2015 Oct 25. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26583122 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog signaling and the axial patterning of Drosophila wings.Biochem Cell Biol. 2000;78(5):585-91. doi: 10.1139/o00-072. Biochem Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11103949 Review.
-
Haltere development in D. melanogaster: implications for the evolution of appendage size, shape and function.Int J Dev Biol. 2020;64(1-2-3):159-165. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.190133LS. Int J Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32659004 Review.
Cited by
-
JNK signaling coordinates with ecdysone signaling to promote pruning of Drosophila sensory neuron dendrites.Development. 2019 Apr 17;146(8):dev163592. doi: 10.1242/dev.163592. Development. 2019. PMID: 30936183 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Human Mutant Preproinsulins Induced Unfolded Protein Response, Gadd45 Expression, JAK-STAT Activation, and Growth Inhibition in Drosophila.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 7;22(21):12038. doi: 10.3390/ijms222112038. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769468 Free PMC article.
-
The NDNF-like factor Nord is a Hedgehog-induced extracellular BMP modulator that regulates Drosophila wing patterning and growth.Elife. 2022 Jan 17;11:e73357. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73357. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35037619 Free PMC article.
-
Rab5 and Rab11 maintain hematopoietic homeostasis by restricting multiple signaling pathways in Drosophila.Elife. 2021 Feb 9;10:e60870. doi: 10.7554/eLife.60870. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33560224 Free PMC article.
-
ZnT7 RNAi favors RafGOFscrib-/--induced tumor growth and invasion in Drosophila through JNK signaling pathway.Oncogene. 2021 Mar;40(12):2217-2229. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01703-x. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33649534
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

