Calcium Uncaging with Visible Light
- PMID: 26974387
- PMCID: PMC4851165
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5b11606
Calcium Uncaging with Visible Light
Abstract
We have designed a nitroaromatic photochemical protecting group that absorbs visible light in the violet-blue range. The chromophore is a dinitro derivative of bisstyrylthiophene (or BIST) that absorbs light very effectively (ε440 = 66,000 M(-1) cm(-1) and two-photon cross section of 350 GM at 775 nm). We developed a "caged calcium" molecule by conjugation of BIST to a Ca(2+) chelator that upon laser flash photolysis rapidly releases Ca(2+) in <0.2 ms. Using the patch-clamp method the optical probe, loaded with Ca(2+), was delivered into acutely isolated mouse cardiac myocytes, where either one- and two-photon uncaging of Ca(2+) induced highly local or cell-wide physiological Ca(2+) signaling events.
Figures

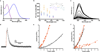

References
-
- Brieke C, Rohrbach F, Gottschalk A, Mayer G, Heckel A. Angew Chem Int Edit. 2012;51:8446–8476. - PubMed
-
- Barltrop JA, Plant PJ, Schofield P. Chem. Commun. 1966:822–823.
-
- Kaplan JH, Forbush B, Hoffman JF. Biochemistry. 1978;17:1929–1935. - PubMed
-
- McGall GH, Barone AD, Diggelmann M, Fodor SPA, Gentalen E, Ngo N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997;119:5081–5090.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

