Environmental Enteric Dysfunction in Children
- PMID: 26974416
- PMCID: PMC4920693
- DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001147
Environmental Enteric Dysfunction in Children
Abstract
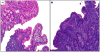
Diarrheal diseases are a major cause of childhood death in resource-poor countries, killing approximately 760,000 children younger than 5 years each year. Although deaths due to diarrhea have declined dramatically, high rates of stunting and malnutrition have persisted. Environmental enteric dysfunction (EED) is a subclinical condition caused by constant fecal-oral contamination with resultant intestinal inflammation and villous blunting. These histological changes were first described in the 1960s, but the clinical effect of EED is only just being recognized in the context of failure of nutritional interventions and oral vaccines in resource-poor countries. We review the existing literature regarding the underlying causes of and potential interventions for EED in children, highlighting the epidemiology, clinical and histologic classification of the entity, and discussing novel biomarkers and possible therapies. Future research priorities are also discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Diarrhoeal disease. 2013 [08/24/2015]. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs330/en/
-
- Adair LS, Fall CH, Osmond C, Stein AD, Martorell R, Ramirez-Zea M, et al. Associations of linear growth and relative weight gain during early life with adult health and human capital in countries of low and middle income: findings from five birth cohort studies. Lancet. 2013;382(9891):525–34. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Victora CG, de Onis M, Hallal PC, Blossner M, Shrimpton R. Worldwide timing of growth faltering: revisiting implications for interventions. Pediatrics. 2010;125(3):e473–80. - PubMed
-
- Bhutta ZA, Ahmed T, Black RE, Cousens S, Dewey K, Giugliani E, et al. What works? Interventions for maternal and child undernutrition and survival. Lancet. 2008;371(9610):417–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

