Development of thieno- and benzopyrimidinone inhibitors of the Hedgehog signaling pathway reveals PDE4-dependent and PDE4-independent mechanisms of action
- PMID: 26976215
- PMCID: PMC5147493
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.03.013
Development of thieno- and benzopyrimidinone inhibitors of the Hedgehog signaling pathway reveals PDE4-dependent and PDE4-independent mechanisms of action
Abstract
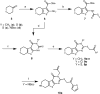
From a high content in vivo screen for modulators of developmental patterning in embryonic zebrafish, we previously identified eggmanone (EGM1, 3) as a Hedgehog (Hh) signaling inhibitor functioning downstream of Smoothened. Phenotypic optimization studies for in vitro probe development utilizing a Gli transcription-linked stable luciferase reporter cell line identified EGM1 analogs with improved potency and aqueous solubility. Mechanistic profiling of optimized analogs indicated two distinct scaffold clusters: PDE4 inhibitors able to inhibit downstream of Sufu, and PDE4-independent Hh inhibitors functioning between Smo and Sufu. Each class represents valuable in vitro probes for elucidating the complex mechanisms of Hh regulation.
Keywords: Eggmanone; Hedgehog signaling pathway; Phenotypic screening; Probe development; Suppressor of Fused.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
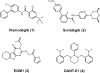




Similar articles
-
An in vivo chemical genetic screen identifies phosphodiesterase 4 as a pharmacological target for hedgehog signaling inhibition.Cell Rep. 2015 Apr 7;11(1):43-50. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 25818300 Free PMC article.
-
The BET bromodomain inhibitor I-BET151 acts downstream of smoothened protein to abrogate the growth of hedgehog protein-driven cancers.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 19;289(51):35494-502. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.595348. Epub 2014 Oct 29. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25355313 Free PMC article.
-
Cilium-independent regulation of Gli protein function by Sufu in Hedgehog signaling is evolutionarily conserved.Genes Dev. 2009 Aug 15;23(16):1910-28. doi: 10.1101/gad.1794109. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19684112 Free PMC article.
-
Current trends in Hedgehog signaling pathway inhibition by small molecules.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018 Oct 15;28(19):3131-3140. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.08.033. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018. PMID: 30177379 Review.
-
Hedgehog signaling pathway: a novel model and molecular mechanisms of signal transduction.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Apr;73(7):1317-32. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2127-4. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26762301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Design of Hedgehog pathway inhibitors for cancer treatment.Med Res Rev. 2019 May;39(3):1137-1204. doi: 10.1002/med.21555. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Med Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 30484872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P60 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL104040/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY008126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL104040/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK58404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EY08126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM062459/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007411/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK59637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM118557/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM115305/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

