Effect of Surotomycin, a Novel Cyclic Lipopeptide Antibiotic, on Intestinal Colonization with Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Mice
- PMID: 26976870
- PMCID: PMC4879352
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02904-15
Effect of Surotomycin, a Novel Cyclic Lipopeptide Antibiotic, on Intestinal Colonization with Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Mice
Abstract
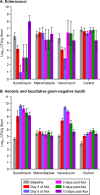
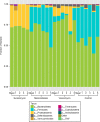
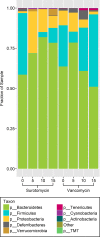
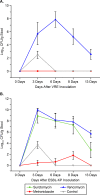
Surotomycin (formerly called CB-183,315) is a novel, orally administered cyclic lipopeptide antibacterial in development for the treatment of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) that has potent activity against vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) but limited activity against Gram-negative bacilli, including Bacteroides spp. We used a mouse model to investigate the impact of surotomycin exposure on the microbiome, and to test the consequences of the disruption on colonization by vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae (ESBL-KP), in comparison with the effects of oral vancomycin and metronidazole. Mice (8 per group) received saline, vancomycin, metronidazole, or surotomycin through an orogastric tube daily for 5 days and were challenged with 10(5) CFU of VRE or ESBL-KP administered through an orogastric tube on day 2 of treatment. The concentrations of the pathogens in stool were determined during and after treatment by plating on selective media. A second experiment was conducted to determine if the antibiotics would inhibit established VRE colonization. In comparison to controls, oral vancomycin promoted VRE and ESBL-KP overgrowth in stool (8 log10 to 10 log10 CFU/g; P < 0.001), whereas metronidazole did not (<4 log10 CFU/g; P > 0.5). Surotomycin promoted ESBL-KP overgrowth (>8 log10 CFU/g; P, <0.001 for comparison with saline controls) but not VRE overgrowth. Surotomycin suppressed preexisting VRE colonization, whereas metronidazole and vancomycin did not. These results suggest that treatment of CDI with surotomycin could reduce levels of VRE acquisition and overgrowth from those with agents such as vancomycin and metronidazole. However, surotomycin and vancomycin may promote colonization by antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative bacilli.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of Fidaxomicin versus Vancomycin on Susceptibility to Intestinal Colonization with Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Mice.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jun 20;60(7):3988-93. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02590-15. Print 2016 Jul. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27090175 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of oral ramoplanin for inhibition of intestinal colonization by vancomycin-resistant enterococci in mice.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Jun;48(6):2144-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.6.2144-2148.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15155213 Free PMC article.
-
Surotomycin demonstrates low in vitro frequency of resistance and rapid bactericidal activity in Clostridium difficile, Enterococcus faecalis, and Enterococcus faecium.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Jul;58(7):3976-82. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00124-14. Epub 2014 May 5. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24798273 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and development of surotomycin for the treatment of Clostridium difficile.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Mar;43(2-3):195-204. doi: 10.1007/s10295-015-1714-6. Epub 2015 Dec 15. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26670919 Review.
-
Surotomycin (A Novel Cyclic Lipopeptide) vs. Vancomycin for the Treatment of Clostridioides difficile Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2019;14(3):166-174. doi: 10.2174/1574884714666190328162637. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30924421
Cited by
-
European Practice for CDI Treatment.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1435:57-84. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-42108-2_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38175471
-
Novel Antimicrobials for the Treatment of Clostridium difficile Infection.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Apr 16;5:96. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00096. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29713630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Experimental and Off-Label Therapies for Clostridium difficile Infection.Infect Dis Ther. 2017 Mar;6(1):1-35. doi: 10.1007/s40121-016-0140-z. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Infect Dis Ther. 2017. PMID: 27910000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tapering Courses of Oral Vancomycin Induce Persistent Disruption of the Microbiota That Provide Colonization Resistance to Clostridium difficile and Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci in Mice.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Apr 26;62(5):e02237-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02237-17. Print 2018 May. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29530853 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Surotomycin on the Gut Microbiota of Healthy Volunteers in a Phase 1 Clinical Trial.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Mar 25;60(4):2069-74. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02531-15. Print 2016 Apr. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 26787687 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Louie TJ, Cannon K, Byrne B, Emery J, Ward L, Eyben M, Krulicki W. 2012. Fidaxomicin preserves the intestinal microbiome during and after treatment of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) and reduces both toxin reexpression and recurrence of CDI. Clin Infect Dis 55(Suppl 2):S132–S142. doi:10.1093/cid/cis338. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tannock GW, Munro K, Taylor C, Lawley B, Young W, Byrne B, Emery J, Louie T. 2010. A new macrocyclic antibiotic, fidaxomicin (OPT-80), causes less alteration to the bowel microbiota of Clostridium difficile-infected patients than does vancomycin. Microbiology 156:3354–3359. doi:10.1099/mic.0.042010-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Nassir W, Sethi AK, Riggs MM, Li Y, Pultz MJ, Donskey CJ. 2008. Both oral metronidazole and oral vancomycin promote persistent overgrowth of vancomycin-resistant enterococci during treatment of Clostridium difficile-associated disease. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:2403–2406. doi:10.1128/AAC.00090-08. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sethi AK, Al-Nassir W, Nerandzic MM, Donskey CJ. 2009. Skin and environmental contamination with vancomycin-resistant enterococci in patients being treated with oral metronidazole versus oral vancomycin for Clostridium difficile-associated disease. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 30:13–17. doi:10.1086/592710. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

