High-fat diet reprograms the epigenome of rat spermatozoa and transgenerationally affects metabolism of the offspring
- PMID: 26977389
- PMCID: PMC4770269
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2015.12.002
High-fat diet reprograms the epigenome of rat spermatozoa and transgenerationally affects metabolism of the offspring
Abstract
Objectives: Chronic and high consumption of fat constitutes an environmental stress that leads to metabolic diseases. We hypothesized that high-fat diet (HFD) transgenerationally remodels the epigenome of spermatozoa and metabolism of the offspring.
Methods: F0-male rats fed either HFD or chow diet for 12 weeks were mated with chow-fed dams to generate F1 and F2 offspring. Motile spermatozoa were isolated from F0 and F1 breeders to determine DNA methylation and small non-coding RNA (sncRNA) expression pattern by deep sequencing.
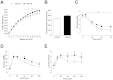
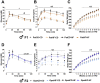
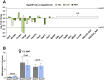
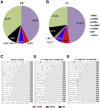
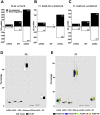
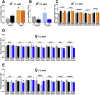
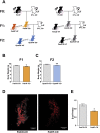
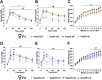
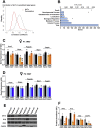
Results: Newborn offspring of HFD-fed fathers had reduced body weight and pancreatic beta-cell mass. Adult female, but not male, offspring of HFD-fed fathers were glucose intolerant and resistant to HFD-induced weight gain. This phenotype was perpetuated in the F2 progeny, indicating transgenerational epigenetic inheritance. The epigenome of spermatozoa from HFD-fed F0 and their F1 male offspring showed common DNA methylation and small non-coding RNA expression signatures. Altered expression of sperm miRNA let-7c was passed down to metabolic tissues of the offspring, inducing a transcriptomic shift of the let-7c predicted targets.
Conclusion: Our results provide insight into mechanisms by which HFD transgenerationally reprograms the epigenome of sperm cells, thereby affecting metabolic tissues of offspring throughout two generations.
Keywords: DNA methylation; Epigenetics; Obesity; Spermatozoa; microRNA.
Figures
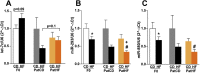



References
-
- Lake J.K., Power C., Cole T.J. Child to adult body mass index in the 1958 British birth cohort: associations with parental obesity. Archives of Disease in Childhood. 1997;77:376–381. - PubMed
-
- Pembrey M.E., Bygren L.O., Kaati G., Edvinsson S., Northstone K., Sjostrom M. Sex-specific, male-line transgenerational responses in humans. European Journal of Human Genetics. 2006;14:159–166. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

