Inducing amnesia through systemic suppression
- PMID: 26977589
- PMCID: PMC4796356
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11003
Inducing amnesia through systemic suppression
Abstract
Hippocampal damage profoundly disrupts the ability to store new memories of life events. Amnesic windows might also occur in healthy people due to disturbed hippocampal function arising during mental processes that systemically reduce hippocampal activity. Intentionally suppressing memory retrieval (retrieval stopping) reduces hippocampal activity via control mechanisms mediated by the lateral prefrontal cortex. Here we show that when people suppress retrieval given a reminder of an unwanted memory, they are considerably more likely to forget unrelated experiences from periods surrounding suppression. This amnesic shadow follows a dose-response function, becomes more pronounced after practice suppressing retrieval, exhibits characteristics indicating disturbed hippocampal function, and is predicted by reduced hippocampal activity. These findings indicate that stopping retrieval engages a suppression mechanism that broadly compromises hippocampal processes and that hippocampal stabilization processes can be interrupted strategically. Cognitively triggered amnesia constitutes an unrecognized forgetting process that may account for otherwise unexplained memory lapses following trauma.
Figures
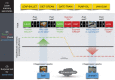

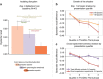
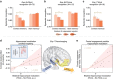
References
-
- Spiers H. J., Maguire E. A. & Burgess N. Hippocampal amnesia. Neurocase 7, 357–382 (2001) . - PubMed
-
- Squire L. R. Memory and the hippocampus: a synthesis from findings with rats, monkeys and humans. Psychol. Rev. 99, 195–231 (1992) . - PubMed
-
- Goshen I. et al. Dynamics of retrieval strategies for remote memories. Cell 147, 678–689 (2011) . - PubMed
-
- Lidsky A. & Slotnick B. M. Electrical stimulation of the hippocampus and electroconvulsive shock produce similar amnestic effects in mice. Neuropsychologia 8, 363–369 (1970) . - PubMed
-
- Anderson M. C. et al. Neural systems underlying the suppression of unwanted memories. Science 303, 232–235 (2004) . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

