Design, Synthesis and Antibacterial Evaluation of Some New 2-Phenyl-quinoline-4-carboxylic Acid Derivatives
- PMID: 26978336
- PMCID: PMC6273947
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21030340
Design, Synthesis and Antibacterial Evaluation of Some New 2-Phenyl-quinoline-4-carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Abstract
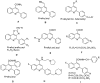
A series of new 2-phenyl-quinoline-4-carboxylic acid derivatives was synthesized starting from aniline, 2-nitrobenzaldehyde, pyruvic acid followed by Doebner reaction, amidation, reduction, acylation and amination. All of the newly-synthesized compounds were characterized by ¹H-NMR, (13)C-NMR and HRMS. The antibacterial activities of these compounds against Gram-negative (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and Gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis), as well as one strain of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria were evaluated by the agar diffusion method (zone of inhibition) and a broth dilution method (minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)), and their structure-activity relationships were obtained and discussed. The results revealed that some compounds displayed good antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, and Compounds 5a₄ and 5a₇ showed the best inhibition with an MIC value of 64 μg/mL against Staphylococcus aureus and with an MIC value of 128 μg/mL against Escherichia coli, respectively. The results of the MTT assay illustrated the low cytotoxicity of Compound 5a4.
Keywords: 2-phenyl-quinoline-4-carboxylic acid derivatives; Doebner reaction; antibacterial activity; synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Khalaj A., Nakhjiri M., Negahbani A.S., Samadizadeh M., Firoozpour L., Rajabalian S., Samadi N., Faramarzi M.A., Adibpour N., Shafiee A., et al. Discovery of a novel nitroimidazolyl-oxazolidinone hybrid with potent anti Gram-positive activity: Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011;46:65–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.10.015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical