Nephrotoxicity of cisplatin combination chemotherapy in thoracic malignancy patients with CKD risk factors
- PMID: 26979596
- PMCID: PMC4793503
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2271-8
Nephrotoxicity of cisplatin combination chemotherapy in thoracic malignancy patients with CKD risk factors
Abstract
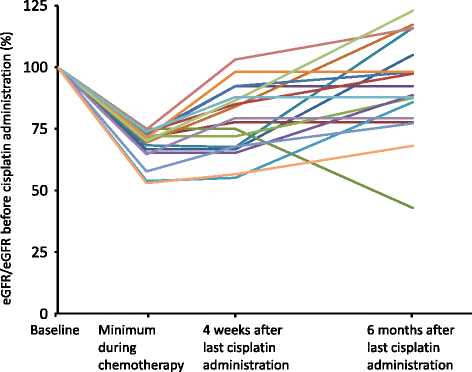
Background: Nephrotoxicity is the major side effect that limits the dose of cisplatin that can be safely administered, and it is a clinical problem in cancer patients who received cisplatin combination chemotherapy. Recent evidence has demonstrated that patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have an increased risk of developing acute kidney injury (AKI). The present study was conducted to evaluate the prevalence of CKD risk factors in patients who received cisplatin and to assess the correlation between CKD risk factors and cisplatin-induced AKI.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 84 patients treated with cisplatin combination chemotherapy for thoracic malignancies. AKI was defined as a decrease in the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) > 25% from base line, an increase in the serum creatinine (sCre) level of > 0.3 mg/dl or ≥ 1.5 times the baseline level.
Results: Eighty of the 84 patients (95.2%) had at least one risk factor for CKD. All enrolled patients received cisplatin with hydration, magnesium supplementation and mannitol. Cisplatin-induced AKI was observed in 18 patients (21.4%). Univariate analysis revealed that cardiac disease and use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) were associated with cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity (odds ratios [OR] 6 and 3.56, 95% confidence intervals [CI] 1.21-29.87 and 1.11-11.39, p = 0.04 and p = 0.04, respectively). Multivariate analysis revealed that cisplatin nephrotoxicity occurred significantly more often in patients with both risk factors (OR 13.64, 95% CI 1.11-326.83, p = 0.04). Patients with more risk factors for CKD tended to have a greater risk of developing cisplatin-induced AKI.
Conclusions: We should consider avoiding administration of cisplatin to patients with CKD risk factors, particularly cardiac disease and NSAID use.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Chronic kidney disease; Cisplatin; Nephrotoxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Ardizzoni A, Boni L, Tiseo M, Fossella FV, Schiller JH, Paesmans M, Radosavljevic D, Paccagnella A, Zatloukal P, Mazzanti P, et al. Cisplatin- versus carboplatin-based chemotherapy in first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: an individual patient data meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99(11):847–57. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djk196. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous