ncRNA orthologies in the vertebrate lineage
- PMID: 26980512
- PMCID: PMC4792531
- DOI: 10.1093/database/bav127
ncRNA orthologies in the vertebrate lineage
Abstract
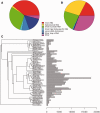
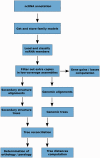
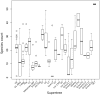
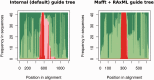
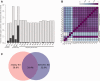
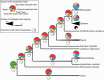
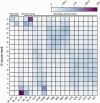
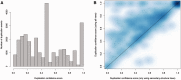
Annotation of orthologous and paralogous genes is necessary for many aspects of evolutionary analysis. Methods to infer these homology relationships have traditionally focused on protein-coding genes and evolutionary models used by these methods normally assume the positions in the protein evolve independently. However, as our appreciation for the roles of non-coding RNA genes has increased, consistently annotated sets of orthologous and paralogous ncRNA genes are increasingly needed. At the same time, methods such as PHASE or RAxML have implemented substitution models that consider pairs of sites to enable proper modelling of the loops and other features of RNA secondary structure. Here, we present a comprehensive analysis pipeline for the automatic detection of orthologues and paralogues for ncRNA genes. We focus on gene families represented in Rfam and for which a specific covariance model is provided. For each family ncRNA genes found in all Ensembl species are aligned using Infernal, and several trees are built using different substitution models. In parallel, a genomic alignment that includes the ncRNA genes and their flanking sequence regions is built with PRANK. This alignment is used to create two additional phylogenetic trees using the neighbour-joining (NJ) and maximum-likelihood (ML) methods. The trees arising from both the ncRNA and genomic alignments are merged using TreeBeST, which reconciles them with the species tree in order to identify speciation and duplication events. The final tree is used to infer the orthologues and paralogues following Fitch's definition. We also determine gene gain and loss events for each family using CAFE. All data are accessible through the Ensembl Comparative Genomics ('Compara') API, on our FTP site and are fully integrated in the Ensembl genome browser, where they can be accessed in a user-friendly manner. Database URL: http://www.ensembl.org.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


Similar articles
-
OGS2: genome re-annotation of the jewel wasp Nasonia vitripennis.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 25;17(1):678. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2886-9. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27561358 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of vertebrate genes related to prion and Shadoo proteins--clues from comparative genomic analysis.Mol Biol Evol. 2004 Dec;21(12):2210-31. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh245. Epub 2004 Sep 1. Mol Biol Evol. 2004. PMID: 15342797
-
Ensembl Genomes 2020-enabling non-vertebrate genomic research.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jan 8;48(D1):D689-D695. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz890. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31598706 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary impact of transposable elements on genomic diversity and lineage-specific innovation in vertebrates.Chromosome Res. 2015 Sep;23(3):505-31. doi: 10.1007/s10577-015-9493-5. Chromosome Res. 2015. PMID: 26395902 Review.
-
An Ariadne's thread to the identification and annotation of noncoding RNAs in eukaryotes.Brief Bioinform. 2009 Sep;10(5):475-89. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbp022. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Brief Bioinform. 2009. PMID: 19383843 Review.
Cited by
-
RNAcentral 2021: secondary structure integration, improved sequence search and new member databases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jan 8;49(D1):D212-D220. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa921. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33106848 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptomics in human and mouse.Nat Rev Genet. 2017 Jul;18(7):425-440. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2017.19. Epub 2017 May 8. Nat Rev Genet. 2017. PMID: 28479595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical analysis of descriptive microRNA data in the translational research on cardioprotection and cardiac repair: lost in the complexity of bioinformatics.Basic Res Cardiol. 2025 Jun;120(3):443-472. doi: 10.1007/s00395-025-01104-1. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Basic Res Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40205177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Controlling metastatic cancer: the role of phytochemicals in cell signaling.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019 May;145(5):1087-1109. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-02892-5. Epub 2019 Mar 22. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30903319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
H/ACA snoRNA levels are regulated during stem cell differentiation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Sep 4;48(15):8686-8703. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa612. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32710630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kishore S., Stamm S. (2006) The snoRNA HBII-52 regulates alternative splicing of the serotonin receptor 2C. Science, 311, 230–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

