Distinct Biochemical Activities of Eyes absent During Drosophila Eye Development
- PMID: 26980695
- PMCID: PMC4793267
- DOI: 10.1038/srep23228
Distinct Biochemical Activities of Eyes absent During Drosophila Eye Development
Abstract
Eyes absent (Eya) is a highly conserved transcriptional coactivator and protein phosphatase that plays vital roles in multiple developmental processes from Drosophila to humans. Eya proteins contain a PST (Proline-Serine-Threonine)-rich transactivation domain, a threonine phosphatase motif (TPM), and a tyrosine protein phosphatase domain. Using a genomic rescue system, we find that the PST domain is essential for Eya activity and Dac expression, and the TPM is required for full Eya function. We also find that the threonine phosphatase activity plays only a minor role during Drosophila eye development and the primary function of the PST and TPM domains is transactivation that can be largely substituted by the heterologous activation domain VP16. Along with our previous results that the tyrosine phosphatase activity of Eya is dispensable for normal Eya function in eye formation, we demonstrate that a primary function of Eya during Drosophila eye development is as a transcriptional coactivator. Moreover, the PST/TPM and the threonine phosphatase activity are not required for in vitro interaction between retinal determination factors. Finally, this work is the first report of an Eya-Ey physical interaction. These findings are particularly important because they highlight the need for an in vivo approach that accurately dissects protein function.
Figures

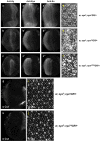

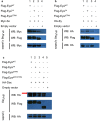
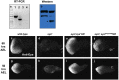
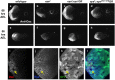


References
-
- Pappu K. S. & Mardon G. Genetic control of retinal specification and determination in Drosophila. Int J Dev Biol 48, 913–924 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Czerny T. et al.. Twin of eyeless, a second Pax-6 gene of Drosophila, acts upstream of eyeless in the control of eye development. Mol Cell 3, 297–307 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Quiring R., Walldorf U., Kloter U. & Gehring W. J. Homology of the eyeless gene of Drosophila to the Small eye gene in mice and Aniridia in humans. Science 265, 785–789 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Bonini N. M., Leiserson W. M. & Benzer S. The eyes absent gene: genetic control of cell survival and differentiation in the developing Drosophila eye. Cell 72, 379–395 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Cheyette B. N. et al.. The Drosophila sine oculis locus encodes a homeodomain-containing protein required for the development of the entire visual system. Neuron 12, 977–996 (1994). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

