Cancer Stem Cells and Macrophages: Implications in Tumor Biology and Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 26980947
- PMCID: PMC4769767
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/9012369
Cancer Stem Cells and Macrophages: Implications in Tumor Biology and Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
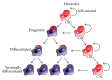
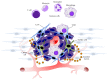
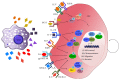
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a unique subset of cells within tumors with stemlike properties that have been proposed to be key drivers of tumor initiation and progression. CSCs are functionally defined by their unlimited self-renewal capacity and their ability to initiate tumor formation in vivo. Like normal stem cells, CSCs exist in a cellular niche comprised of numerous cell types including tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) which provides a unique microenvironment to protect and promote CSC functions. TAMs provide pivotal signals to promote CSC survival, self-renewal, maintenance, and migratory ability, and in turn, CSCs deliver tumor-promoting cues to TAMs that further enhance tumorigenesis. Studies in the last decade have aimed to understand the molecular mediators of CSCs and TAMs, and recent advances have begun to elucidate the complex cross talk that occurs between these two cell types. In this review, we discuss the molecular interactions that define CSC-TAM cross talk at each stage of tumor progression and examine the clinical implications of targeting these interactions.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

