Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Suppresses Apoptosis and Promotes Renal Tubular Regeneration After Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats
- PMID: 26981502
- PMCID: PMC4780282
- DOI: 10.5812/numonthly.34421
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Suppresses Apoptosis and Promotes Renal Tubular Regeneration After Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats
Abstract
Background: Renal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury remains a major cause of acute kidney injury (AKI), in addition to I/R injury-induced tissue inflammation, necrosis and apoptosis. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO) is defined as a treatment in which a patient is intermittently exposed to 100% oxygen pressurized to a pressure above sea level (> 2.0 atmospheres absolute (ATA), 1.0 ATA = 760 mmHg). It has been used in a number of medical conditions with a proven efficacy in a limited number of disorders. However, the effects of HBO therapy on apoptosis and proliferative activity after I/R injury have not been fully understood.
Objectives: We studied the possible beneficial effects of HBO therapy on apoptosis and tubular cell regeneration after renal I/R injury in rats.
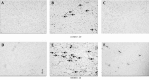
Materials and methods: Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomized into three groups: Sham (Sham-operated rats); I/R (animals submitted to I/R); and I/R + HBO (I/R rats exposed to HBO). Tubular cell apoptosis was confirmed by DNA laddering and the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated uridine triphosphate nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay. Cellular proliferation activity was determined using the anti-Ki-67 antibody.
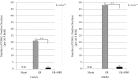
Results: A significant decrease in apoptotic cells and increase in proliferative reaction were observed in the I/R + HBO group compared to the I/R group.
Conclusions: We demonstrated that HBO suppressed apoptosis, which caused inflammation after renal I/R, and promoted tubular cell regeneration. HBO has protective effects against AKI caused by renal I/R through the inhibition of apoptosis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy; Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury; Rats.
Figures

References
-
- Lieberthal W, Triaca V, Koh JS, Pagano PJ, Levine JS. Role of superoxide in apoptosis induced by growth factor withdrawal. Am J Physiol. 1998;275(5 Pt 2):F691–702. - PubMed
-
- Rubinstein I, Abassi Z, Milman F, Ovcharenko E, Coleman R, Winaver J, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment improves GFR in rats with ischaemia/reperfusion renal injury: a possible role for the antioxidant/oxidant balance in the ischaemic kidney. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24(2):428–36. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn511. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
