Serum Sclerostin Levels in Patients with Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection and Their Association with Bone Turnover Markers and Bone Mineral Densitometry
- PMID: 26981516
- PMCID: PMC4791433
- DOI: 10.11005/jbm.2016.23.1.16
Serum Sclerostin Levels in Patients with Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection and Their Association with Bone Turnover Markers and Bone Mineral Densitometry
Abstract
Background: The aim of the study was to compare serum sclerostin levels in human im-munodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected patients and healthy controls, and to evaluate their relationship with bone turnover markers (BTM) and bone mineral density (BMD).
Methods: We prospectively studied 33 HIV treatment-naive patients and 63 healthy individuals; matched for age and sex. Serum sclerostin levels, BTM, BMD were measured. Viral load and cluster of differentiation 4 (CD4) levels were also assessed in HIV-infected patients.
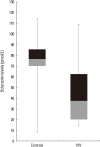
Results: The mean±standard deviation (SD) age of sample was 37.6±10.3 years (range, 19 to 59 years). Of the 96 subjects, 58 (60.4%) were male and 38 (39.6%) were female. Infection with HIV is associated with significant reduction in serum sclerostin levels (HIV-infected: 39.4±28.3 vs. non HIV: 76.6±15.7 pmol/L; P<0.001) and a decrease in BMD at femoral neck and lumbar spine compared to healthy controls. Sclerostin however was not correlated with BMD and was not related to age, generally a strong correlation. There were no significant correlations between sclerostin and BTM (P>0.05).
Conclusions: These findings suggest that untreated HIV and the resulting immune deficiency and/or systemic inflammation could be an important regulator of serum sclerostin in this population.
Keywords: Glycoproteins; HIV; Osteoporosis; Saudi Arabia.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Yong MK, Elliott JH, Woolley IJ, et al. Low CD4 count is associated with an increased risk of fragility fracture in HIV-infected patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011;57:205–210. - PubMed
-
- Borderi M, Gibellini D, Vescini F, et al. Metabolic bone disease in HIV infection. AIDS. 2009;23:1297–1310. - PubMed
-
- Cazanave C, Dupon M, Lavignolle-Aurillac V, et al. Reduced bone mineral density in HIV-infected patients: prevalence and associated factors. AIDS. 2008;22:395–402. - PubMed
-
- Fausto A, Bongiovanni M, Cicconi P, et al. Potential predictive factors of osteoporosis in HIV-positive subjects. Bone. 2006;38:893–897. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

