Loss of B Cells in Patients with Heterozygous Mutations in IKAROS
- PMID: 26981933
- PMCID: PMC4836293
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1512234
Loss of B Cells in Patients with Heterozygous Mutations in IKAROS
Abstract
Background: Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is characterized by late-onset hypogammaglobulinemia in the absence of predisposing factors. The genetic cause is unknown in the majority of cases, and less than 10% of patients have a family history of the disease. Most patients have normal numbers of B cells but lack plasma cells.
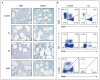
Methods: We used whole-exome sequencing and array-based comparative genomic hybridization to evaluate a subset of patients with CVID and low B-cell numbers. Mutant proteins were analyzed for DNA binding with the use of an electrophoretic mobility-shift assay (EMSA) and confocal microscopy. Flow cytometry was used to analyze peripheral-blood lymphocytes and bone marrow aspirates.
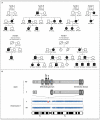
Results: Six different heterozygous mutations in IKZF1, the gene encoding the transcription factor IKAROS, were identified in 29 persons from six families. In two families, the mutation was a de novo event in the proband. All the mutations, four amino acid substitutions, an intragenic deletion, and a 4.7-Mb multigene deletion involved the DNA-binding domain of IKAROS. The proteins bearing missense mutations failed to bind target DNA sequences on EMSA and confocal microscopy; however, they did not inhibit the binding of wild-type IKAROS. Studies in family members showed progressive loss of B cells and serum immunoglobulins. Bone marrow aspirates in two patients had markedly decreased early B-cell precursors, but plasma cells were present. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia developed in 2 of the 29 patients.
Conclusions: Heterozygous mutations in the transcription factor IKAROS caused an autosomal dominant form of CVID that is associated with a striking decrease in B-cell numbers. (Funded by the National Institutes of Health and others.).
Figures

References
-
- Gathmann B, Mahlaoui N, Gérard L, et al. Clinical picture and treatment of 2212 patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:116–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI-061093/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006542/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG006542/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI104857/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AI086037/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-094004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-104857/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI061093/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- T32 GM007280/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI101093/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- TR-000043/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- AI-086037/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000043/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- AI-101093/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32-GM007280/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- Z99 CL999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R18 AI048693/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI094004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-48693/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
