The amino acid sensor GCN2 controls gut inflammation by inhibiting inflammasome activation
- PMID: 26982722
- PMCID: PMC4854628
- DOI: 10.1038/nature17186
The amino acid sensor GCN2 controls gut inflammation by inhibiting inflammasome activation
Abstract
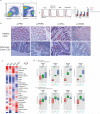
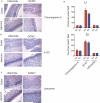
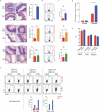
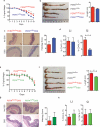
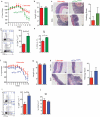
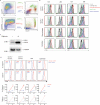
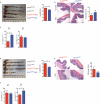
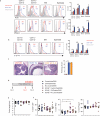
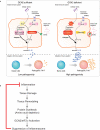
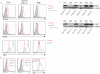
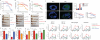
The integrated stress response (ISR) is a homeostatic mechanism by which eukaryotic cells sense and respond to stress-inducing signals, such as amino acid starvation. General controlled non-repressed (GCN2) kinase is a key orchestrator of the ISR, and modulates protein synthesis in response to amino acid starvation. Here we demonstrate in mice that GCN2 controls intestinal inflammation by suppressing inflammasome activation. Enhanced activation of ISR was observed in intestinal antigen presenting cells (APCs) and epithelial cells during amino acid starvation, or intestinal inflammation. Genetic deletion of Gcn2 (also known as Eif2ka4) in CD11c(+) APCs or intestinal epithelial cells resulted in enhanced intestinal inflammation and T helper 17 cell (TH17) responses, owing to enhanced inflammasome activation and interleukin (IL)-1β production. This was caused by reduced autophagy in Gcn2(-/-) intestinal APCs and epithelial cells, leading to increased reactive oxygen species (ROS), a potent activator of inflammasomes. Thus, conditional ablation of Atg5 or Atg7 in intestinal APCs resulted in enhanced ROS and TH17 responses. Furthermore, in vivo blockade of ROS and IL-1β resulted in inhibition of TH17 responses and reduced inflammation in Gcn2(-/-) mice. Importantly, acute amino acid starvation suppressed intestinal inflammation via a mechanism dependent on GCN2. These results reveal a mechanism that couples amino acid sensing with control of intestinal inflammation via GCN2.
Figures
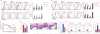


Comment in
-
Amino acid deprivation promotes intestinal homeostasis through autophagy.Oncotarget. 2016 May 24;7(21):29877-8. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8841. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27105494 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zhou R, Yazdi AS, Menu P, Tschopp J. A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature. 2011;469:221–225. doi:10.1038/nature09663. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity. 2011;34:637–650. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.05.006. - PubMed
-
- Pulendran B. The Varieties of Immunological Experience:Of Pathogens, Stress, and Dendritic Cells. Annual Review of Immunology. 2015 Apr;33 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U19 AI090023/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI057266/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK042394/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI048638/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA ES103286/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK057665/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL052173/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103185/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI048638/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK088227/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050409/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R38 AI140299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

