Targeted Rho-associated kinase 2 inhibition suppresses murine and human chronic GVHD through a Stat3-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 26983850
- PMCID: PMC4850869
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-10-678706
Targeted Rho-associated kinase 2 inhibition suppresses murine and human chronic GVHD through a Stat3-dependent mechanism
Abstract
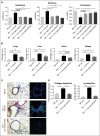
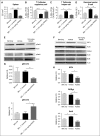
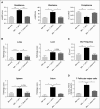
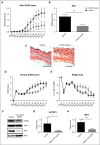
Chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) remains a major complication following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT). The discovery of novel therapeutics is dependent on assessment in preclinical murine models of cGVHD. Rho-associated kinase 2 (ROCK2) recently was shown to be implicated in regulation of interleukin-21 (IL-21) and IL-17 secretion in mice and humans. Here, we report that the selective ROCK2 inhibitor KD025 effectively ameliorates cGVHD in multiple models: a full major histocompatibility complex (MHC) mismatch model of multiorgan system cGVHD with bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome and a minor MHC mismatch model of sclerodermatous GVHD. Treatment with KD025 resulted in normalization of pathogenic pulmonary function, which correlates with a marked reduction of antibody and collagen deposition in the lungs of treated mice to levels comparable to non-cGVHD controls. Spleens of mice treated with KD025 had decreased frequency of T follicular helper cells and increased frequency of T follicular regulatory cells, accompanied by a reduction in signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and concurrent increase in STAT5 phosphorylation. The critical role of STAT3 in this cGVHD model was confirmed by data showing that mice transplanted with inducible STAT3-deficient T cells had pulmonary function comparable to the healthy negative controls. The therapeutic potential of targeted ROCK2 inhibition in the clinic was solidified further by human data demonstrating the KD025 inhibits the secretion of IL-21, IL-17, and interferon γ along with decreasing phosphorylated STAT3 and reduced protein expression of interferon regulatory factor 4 and B-cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6) in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells purified from active cGVHD patients. Together these data highlight the potential of targeted ROCK2 inhibition for clinical cGVHD therapy.
© 2016 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures

References
-
- Lee SJ, Klein JP, Barrett AJ, et al. Severity of chronic graft-versus-host disease: association with treatment-related mortality and relapse. Blood. 2002;100(2):406–414. - PubMed
-
- Flowers ME, Parker PM, Johnston LJ, et al. Comparison of chronic graft-versus-host disease after transplantation of peripheral blood stem cells versus bone marrow in allogeneic recipients: long-term follow-up of a randomized trial. Blood. 2002;100(2):415–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

