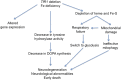
A role for iron deficiency in dopaminergic neurodegeneration
- PMID: 26984501
- PMCID: PMC4822629
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1601976113
A role for iron deficiency in dopaminergic neurodegeneration
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment on
-
Disrupted iron homeostasis causes dopaminergic neurodegeneration in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Mar 29;113(13):3428-35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1519473113. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26929359 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Comparative study of the influence of Thy1 deficiency and dietary iron deficiency on dopaminergic profiles in the mouse striatum.J Neurosci Res. 2008 Nov 1;86(14):3194-202. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21758. J Neurosci Res. 2008. PMID: 18615641
-
Minimal brain damage induced by early iron deficiency: modified dopaminergic neurotransmission.Isr J Med Sci. 1987 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):19-25. Isr J Med Sci. 1987. PMID: 3032848
-
[Iron deficiency and vitamin B12 deficiency and their combination].Munch Med Wochenschr. 1955 Sep 9;97(36):1177-8. Munch Med Wochenschr. 1955. PMID: 13265712 German. No abstract available.
-
Iron metabolism: iron deficiency and iron overload.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2000;1:75-98. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.1.1.75. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 11701625 Review.
-
Iron status and neural functioning.Annu Rev Nutr. 2003;23:41-58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.23.020102.075739. Epub 2003 Apr 10. Annu Rev Nutr. 2003. PMID: 12704220 Review.
Cited by
-
Iron Redox Chemistry and Implications in the Parkinson's Disease Brain.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Oct 9;2019:4609702. doi: 10.1155/2019/4609702. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31687080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gestational iron supplementation reverses depressive-like behavior in post-partum Sprague Dawley rats: Evidence from behavioral and neurohistological studies.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022 Apr 20;12:280-296. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2022.04.004. eCollection 2022 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35746978 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal Ethanol Exposure Misregulates Genes Involved in Iron Homeostasis Promoting a Maladaptation of Iron Dependent Hippocampal Synaptic Transmission and Plasticity.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 7;10:1312. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01312. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31787896 Free PMC article.
-
A commentary on studies of brain iron accumulation during ageing.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2024 Jun;29(4):385-394. doi: 10.1007/s00775-024-02060-2. Epub 2024 May 12. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 38735007 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang Z, et al. Pro-inflammatory cytokine-mediated ferroportin down-regulation contributes to the nigral iron accumulation in lipopolysaccharide-induced Parkinsonian models. Neuroscience. 2014;257:20–30. - PubMed
-
- You LH, et al. Brain iron accumulation exacerbates the pathogenesis of MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience. 2015;284:234–246. - PubMed
-
- Crichton RR, Dexter DT, Ward RJ. Brain iron metabolism and its perturbation in neurological diseases. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2011;118(3):301–314. - PubMed
-
- Rouault TA. Iron metabolism in the CNS: Implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013;14(8):551–564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources