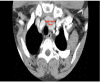
Missed retrosternal ectopic thyroid tissue in a patient operated for multinodular goiter
- PMID: 26985161
- PMCID: PMC4771431
- DOI: 10.5152/UCD.2015.2916
Missed retrosternal ectopic thyroid tissue in a patient operated for multinodular goiter
Abstract
Ectopic thyroid tissue has been found from the tongue to the diaphragm. The most common ectopic thyroid tissue has been found in the tongue, submandibular region, cervical lymph nodes, larynx, trachea, oesophagus, mediastinum, diaphragm and heart respectively. "Forgotten goiter" is an extremely rare disease which is defined as a mediastinal thyroid mass found after total thyroidectomy. In this case report, we discussed a 49 year-old female patient whose retrosternal ectopic thyroid tissue was detected by thyroid scintigraphy taken in postoperative period after total thyroidectomy performed with diagnosis of multinodular goiter. Papillary carcinoma was determined by the histopathological examination. Ectopic thyroid tissue was removed by performing sternotomy. We did not observe any postoperative surgical complications. 100 mCi dose of radioactive iodine was administered to the patient. Retrosternal ectopic thyroid tissue detected after total thyroidectomy is a rarely encountered condition. Therefore, retrosternal ectopic thyroid tissue existence should be definitely kept in mind in patients with no increase in thyroid stimulating hormone level after total thyroidectomy.
Keywords: Total thyroidectomy; ectopic; goiter; retrosternal; thyroid.
Figures
References
-
- Mace AD, Taghi A, Khalil S, Sandison A. Ectopic sequestered thyroid tissue: An unusual cause of a mediastinal mass. ISRN Surgery. 2011;2011:313626. http://dx.doi.org/10.5402/2011/313626. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shah BC, Ravichand CS, Juluri S, Agarwal A, Pramesh CS, Mistry RC. Ectopic thyroid cancer. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;13:122–124. - PubMed
-
- Radkowski D, Arnold J, Healy GB, McGill T, Treves ST, Paltiel H, et al. Thyroglossal duct remnants. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1991;117:1378–1381. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1991.01870240070011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Calò PG, Tatti A, Medas F, Petruzzo P, Pisano G, Nicolosi A. Forgotten goiter. Our experience and a review of the literature. Ann Ital Chir. 2012;83:487–490. - PubMed
-
- Yorgancilar E, Yildirim M, Gun R, Bakir S, Topcu I. Management to substernal goiter. KBB-Forum. 2011;10:40–45.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources