Risk Factors for Development and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Exploratory Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26986114
- PMCID: PMC4839895
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003013
Risk Factors for Development and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Exploratory Meta-Analysis
Abstract
The risk factors influencing the natural course of chronic kidney disease (CKD) are complex and heterogeneous, and few systematic reviews to date have focused on this issue. The aim of the study is to identify the risk factors for disease development and progression in each stage of CKD. We conducted electronic literature searches of PubMed, MEDLINE, Scopus, and the Cochrane Library up to October 15, 2012, for observational studies evaluating the risk factors on the development or progression of CKD. Eligible studies should have collected repeated information that could evaluate changes in renal function. Extracted information from all the included studies was synthesized narratively. Quality assessments were performed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. An exploratory random-effects meta-analysis was performed where feasible to pool effect sizes across studies for a specific risk factor in a specific outcome. We identified 38 cohort studies and 2 case-control studies from 40 articles, with a total of 318,898 participants from 14 countries. The follow-up duration ranged from 1.5 to 16 years. The majority of the included studies were of high quality. The baseline CKD stages of the included studies ranged from normal to later stages, and only 19 studies could be classified into a specific range of CKD stages during follow-up. Three risk factors from studies of the same baseline and follow-up CKD stages were eligible for the exploratory meta-analysis, including male sex, substantial proteinuria, and diabetes. The hazard ratios for the progression from CKD stages 3-5 to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) were 1.37 (95% confidence interval 1.17-1.62), 1.64 (1.01-2.66), and 1.16 (0.98-1.38) for male sex, substantial proteinuria, and diabetes, respectively. In conclusion, our analyses comprehensively summarize the initiating and perpetuating factors for CKD. Male sex and substantial proteinuria are significant perpetuating factors for the progression from late stage CKD to ESRD, and diabetes may play a minor role for the outcome of ESRD among patients with later stages of CKD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Figures
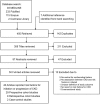

References
-
- James MT, Hemmelgarn BR, Tonelli M. Early recognition and prevention of chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2010; 375:1296–1309. - PubMed
-
- Wen CP, Cheng TY, Tsai MK, et al. All-cause mortality attributable to chronic kidney disease: a prospective cohort study based on 462,293 adults in Taiwan. Lancet 2008; 371:2173–2182. - PubMed
-
- Wu HY, Hung KY, Tu YK, et al. Comparative effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs in patients with diabetes. J Comp Eff Res 2014; 3:213–215. - PubMed
-
- Iseki K, Iseki C, Kinjo K. C-reactive protein is a predictor for developing proteinuria in a screened cohort. Nephron Clin Pract 2011; 117:c51–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

