Aloe vera: A review of toxicity and adverse clinical effects
- PMID: 26986231
- PMCID: PMC6349368
- DOI: 10.1080/10590501.2016.1166826
Aloe vera: A review of toxicity and adverse clinical effects
Abstract
The Aloe plant is employed as a dietary supplement in a variety of foods and as an ingredient in cosmetic products. The widespread human exposure and its potential toxic and carcinogenic activities raise safety concerns. Chemical analysis reveals that the Aloe plant contains various polysaccharides and phenolic chemicals, notably anthraquinones. Ingestion of Aloe preparations is associated with diarrhea, hypokalemia, pseudomelanosis coli, kidney failure, as well as phototoxicity and hypersensitive reactions. Recently, Aloe vera whole leaf extract showed clear evidence of carcinogenic activity in rats, and was classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer as a possible human carcinogen (Group 2B). This review presents updated information on the toxicological effects, including the cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, and adverse clinical effects of Aloe vera whole leaf extract, gel, and latex.
Keywords: Aloe gel; Aloe vera; aloe latex; carcinogenicity; genotoxicity; toxicological effects.
Figures
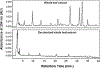
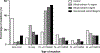
References
-
- Barnes PM, Bloom B, Nahin RL. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults and children: United States, 2007. Natl Health Stat Report. 2008;12:1–23. - PubMed
-
- Nahin RL, Barnes PM, Stussman BJ, Bloom B. Costs of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) and frequency of visits to CAM practitioners: United States, 2007. Natl Health Stat Report. 2009;18:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel (CIR). Final report on the safety assessment of aloe andongensis extract, aloe andongensis leaf juice, aloe arborescens leaf extract, aloe arborescens leaf juice, aloe arborescens leaf protoplasts, aloe barbadensis flower extract, aloe barbadensis leaf, aloe barbadensis leaf extract, aloe barbadensis leaf juice, aloe barbadensis leaf polysaccharides, aloe barbadensis leaf water, aloe ferox leaf extract, aloe ferox leaf juice, and aloe ferox leaf juice extract. Int J Toxicol. 2007;26(Suppl 2):1–50. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez Rodriguez E, Darias Martin J, Diaz Romero C. Aloe vera as a functional ingredient in foods. CritRev Food Sci Nutr. 2010;50:305–326. - PubMed
-
- Boudreau MD, Beland FA. An evaluation of the biological and toxicological properties of Aloe barbadensis (miller), Aloe vera. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2006;24:103–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
