Current artefacts in cardiac and chest magnetic resonance imaging: tips and tricks
- PMID: 26986460
- PMCID: PMC5258161
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20150987
Current artefacts in cardiac and chest magnetic resonance imaging: tips and tricks
Abstract
Currently MRI is extensively used for the evaluation of cardiovascular and thoracic disorders because of the well-established advantages that include use of non-ionizing radiation, good contrast and high spatial resolution. Despite the advantages of this technique, numerous categories of artefacts are frequently encountered. They may be related to the scanner hardware or software functionalities, environmental factors or the human body itself. In particular, some artefacts may be exacerbated with high-field-strength MR machines (e.g. 3 T). Cardiac imaging poses specific challenges with respect to breath-holding and cardiac motion. In addition, new cardiac MR-conditional devices may also be responsible for peculiar artefacts. The image quality may thus be impaired and give rise to a misdiagnosis. Knowledge of acquisition and reconstruction techniques is required to understand and recognize the nature of these artefacts. This article will focus on the origin and appearance of the most common artefacts encountered in cardiac and chest MRI along with possible correcting methods to avoid or reduce them.
Figures
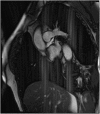
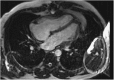

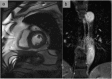

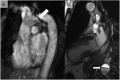
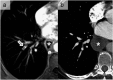
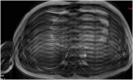
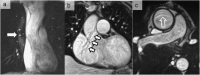
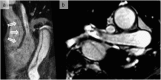
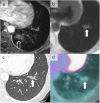

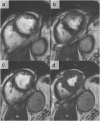
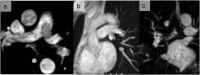
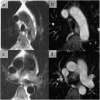
References
-
- Klinke V, Muzzarelli S, Lauriers N, Locca D, Vincenti G, Monney P, et al. . Quality assessment of cardiovascular magnetic resonance in the setting of the European CMR registry: description and validation of standardized criteria. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2013; 15: 55. doi: 10.1186/1532-429X-15-55 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schwitter J, Kanal E, Schmitt M, Anselme F, Albert T, Hayes DL, et al. . Impact of the Advisa MRI pacing system on the diagnostic quality of cardiac MR images and contraction patterns of cardiac muscle during scans: Advisa MRI randomized clinical multicenter study results. Heart Rhythm 2013; 10: 864–72. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2013.02.019 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

