Amelioration of Diabetic Mouse Nephropathy by Catalpol Correlates with Down-Regulation of Grb10 Expression and Activation of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 / Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor Signaling
- PMID: 26986757
- PMCID: PMC4795681
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151857
Amelioration of Diabetic Mouse Nephropathy by Catalpol Correlates with Down-Regulation of Grb10 Expression and Activation of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 / Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor Signaling
Abstract
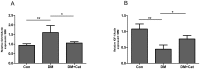
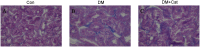
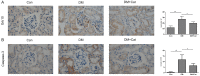
Growth factor receptor-bound protein 10 (Grb10) is an adaptor protein that can negatively regulate the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R). The IGF1-1R pathway is critical for cell growth and apoptosis and has been implicated in kidney diseases; however, it is still unknown whether Grb10 expression is up-regulated and plays a role in diabetic nephropathy. Catalpol, a major active ingredient of a traditional Chinese medicine, Rehmannia, has been reported to possess anti-inflammatory and anti-aging activities and then used to treat diabetes. Herein, we aimed to assess the therapeutic effect of catalpol on a mouse model diabetic nephropathy and the potential role of Grb10 in the pathogenesis of this diabetes-associated complication. Our results showed that catalpol treatment improved diabetes-associated impaired renal functions and ameliorated pathological changes in kidneys of diabetic mice. We also found that Grb10 expression was significantly elevated in kidneys of diabetic mice as compared with that in non-diabetic mice, while treatment with catalpol significantly abrogated the elevated Grb10 expression in diabetic kidneys. On the contrary, IGF-1 mRNA levels and IGF-1R phosphorylation were significantly higher in kidneys of catalpol-treated diabetic mice than those in non-treated diabetic mice. Our results suggest that elevated Grb10 expression may play an important role in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy through suppressing IGF-1/IGF-1R signaling pathway, which might be a potential molecular target of catalpol for the treatment of this diabetic complication.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of catalpol on diabetic nephropathy in rats.Phytomedicine. 2013 Aug 15;20(11):1023-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.04.007. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Phytomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23746755
-
IGF-1 signaling pathway activation promotes axonal regeneration and repair: A mechanism study on catalpol-induced functional recovery after ischemic stroke.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 May 28;348:119808. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119808. Epub 2025 Apr 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40245961
-
Insulin deficiency induces rat renal mesangial cell dysfunction via activation of IGF-1/IGF-1R pathway.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016 Feb;37(2):217-27. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.128. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016. PMID: 26775660 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of insulin and type 1 insulin-like growth factor signaling and action by the Grb10/14 and SH2B1/B2 adaptor proteins.FEBS J. 2013 Feb;280(3):794-816. doi: 10.1111/febs.12080. Epub 2013 Jan 2. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23190452 Review.
-
Grb10 adapter protein as regulator of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling.J Cell Physiol. 2003 Dec;197(3):307-11. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10363. J Cell Physiol. 2003. PMID: 14566960 Review.
Cited by
-
Activating the PGC-1α/TERT Pathway by Catalpol Ameliorates Atherosclerosis via Modulating ROS Production, DNA Damage, and Telomere Function: Implications on Mitochondria and Telomere Link.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Jun 25;2018:2876350. doi: 10.1155/2018/2876350. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30046372 Free PMC article.
-
Catalpol alleviates amyloid- generation and neuronal oxidative stress injury via activating the Keap1-Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in the immortalized lymphocytes from patients with late-onset Alzheimer's disease and SKNMC cells co-culture model.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(12):1547-1557. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2024.78543.16982. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39539442 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and Biochemical Pathways of Catalpol in Alleviating Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 20;11(2):323. doi: 10.3390/biom11020323. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33672590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytotherapy in the Management of Diabetes: A Review.Molecules. 2018 Jan 4;23(1):105. doi: 10.3390/molecules23010105. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29300317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The protective effect and mechanism of catalpol on high glucose-induced podocyte injury.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Sep 5;19(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2656-8. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31488111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- White KE, Bilous RW. Type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy show structural-functional Relationships that are similar to type 1 disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2000;11(9): 1667–1673. - PubMed
-
- System URD: USRDS 2012 Annual Data Report:Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States. Bethesda, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2012.
-
- Han DC, Shen TL, Guan JL. The Grb7 family proteins: Structure, interactions with other signaling molecules and potential cellular functions. Oncogene. 2001;20(44): 6315–6321. - PubMed
-
- Dong LQ, Du H, Porter SG, Kolakowski LF Jr, Lee AV, Mandarino LJ, et al. Cloning, chromosome localization, expression, and characterization of an Src homology 2 and pleckstrin homology domain- containing insulin receptor binding protein hGrb10gamma. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(46): 29104–29112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

