Modulating Innate and Adaptive Immunity by (R)-Roscovitine: Potential Therapeutic Opportunity in Cystic Fibrosis
- PMID: 26987072
- PMCID: PMC4800827
- DOI: 10.1159/000444256
Modulating Innate and Adaptive Immunity by (R)-Roscovitine: Potential Therapeutic Opportunity in Cystic Fibrosis
Abstract
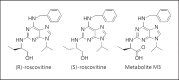
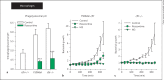
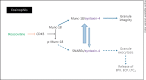
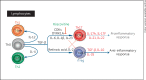
(R)-Roscovitine, a pharmacological inhibitor of kinases, is currently in phase II clinical trial as a drug candidate for the treatment of cancers, Cushing's disease and rheumatoid arthritis. We here review the data that support the investigation of (R)-roscovitine as a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF). (R)-Roscovitine displays four independent properties that may favorably combine against CF: (1) it partially protects F508del-CFTR from proteolytic degradation and favors its trafficking to the plasma membrane; (2) by increasing membrane targeting of the TRPC6 ion channel, it rescues acidification in phagolysosomes of CF alveolar macrophages (which show abnormally high pH) and consequently restores their bactericidal activity; (3) its effects on neutrophils (induction of apoptosis), eosinophils (inhibition of degranulation/induction of apoptosis) and lymphocytes (modification of the Th17/Treg balance in favor of the differentiation of anti-inflammatory lymphocytes and reduced production of various interleukins, notably IL-17A) contribute to the resolution of inflammation and restoration of innate immunity, and (4) roscovitine displays analgesic properties in animal pain models. The fact that (R)-roscovitine has undergone extensive preclinical safety/pharmacology studies, and phase I and II clinical trials in cancer patients, encourages its repurposing as a CF drug candidate.
© 2016 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

Comment in
-
From Starfish Oocytes to Inflammation: The Unforeseeable Destiny of Roscovitine in Cystic Fibrosis.J Innate Immun. 2016;8(4):327-9. doi: 10.1159/000445967. Epub 2016 Apr 26. J Innate Immun. 2016. PMID: 27111672 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
(R)-Roscovitine and CFTR modulators enhance killing of multi-drug resistant Burkholderia cenocepacia by cystic fibrosis macrophages.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 10;10(1):21700. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78817-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33303916 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and pharmacokinetics of Roscovitine (Seliciclib) in cystic fibrosis patients chronically infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a randomized, placebo-controlled study.J Cyst Fibros. 2022 May;21(3):529-536. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2021.10.013. Epub 2021 Dec 24. J Cyst Fibros. 2022. PMID: 34961705 Clinical Trial.
-
Harnessing Neutrophil Survival Mechanisms during Chronic Infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Novel Therapeutic Targets to Dampen Inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jun 30;7:243. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00243. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28713772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roscovitine is a proteostasis regulator that corrects the trafficking defect of F508del-CFTR by a CDK-independent mechanism.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Nov;171(21):4831-49. doi: 10.1111/bph.12859. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25065395 Free PMC article.
-
Dysfunctional Inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis Airways: From Mechanisms to Novel Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 16;22(4):1952. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041952. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669352 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunomodulation in Cystic Fibrosis: Why and How?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 8;21(9):3331. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093331. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32397175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
R-Roscovitine Improves Motoneuron Function in Mouse Models for Spinal Muscular Atrophy.iScience. 2020 Feb 21;23(2):100826. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.100826. Epub 2020 Jan 10. iScience. 2020. PMID: 31981925 Free PMC article.
-
Roscovitine enhances the bactericidal activity of the airway surface liquid of the cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelium but does not protect against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection.PLoS One. 2025 May 5;20(5):e0321996. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0321996. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40323902 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding Neutrophil Horizons: New Concepts in Inflammation.J Innate Immun. 2018;10(5-6):422-431. doi: 10.1159/000493101. Epub 2018 Sep 26. J Innate Immun. 2018. PMID: 30257246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
(R)-Roscovitine and CFTR modulators enhance killing of multi-drug resistant Burkholderia cenocepacia by cystic fibrosis macrophages.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 10;10(1):21700. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78817-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33303916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gaspar MC, Couet W, Olivier JC, Pais AA, Sousa JJ. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis lung disease and new perspectives of treatment: a review. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013;32:1231–1252. - PubMed
-
- Chmiel JF, Aksamit TR, Chotirmall SH, Dasenbrook EC, Elborn JS, LiPuma JJ, Ranganathan SC, Waters VJ, Ratjen FA. Antibiotic management of lung infections in cystic fibrosis. I. The microbiome, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Gram-negative bacteria, and multiple infections. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2014;11:1298–1306. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Savoia D. New perspectives in the management of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Future Microbiol. 2014;9:917–928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

