A CEP215-HSET complex links centrosomes with spindle poles and drives centrosome clustering in cancer
- PMID: 26987684
- PMCID: PMC4802056
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11005
A CEP215-HSET complex links centrosomes with spindle poles and drives centrosome clustering in cancer
Abstract
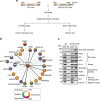
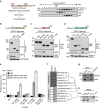
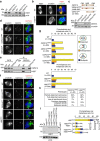
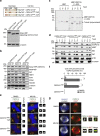
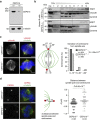
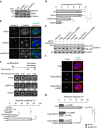
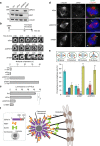
Numerical centrosome aberrations underlie certain developmental abnormalities and may promote cancer. A cell maintains normal centrosome numbers by coupling centrosome duplication with segregation, which is achieved through sustained association of each centrosome with a mitotic spindle pole. Although the microcephaly- and primordial dwarfism-linked centrosomal protein CEP215 has been implicated in this process, the molecular mechanism responsible remains unclear. Here, using proteomic profiling, we identify the minus end-directed microtubule motor protein HSET as a direct binding partner of CEP215. Targeted deletion of the HSET-binding domain of CEP215 in vertebrate cells causes centrosome detachment and results in HSET depletion at centrosomes, a phenotype also observed in CEP215-deficient patient-derived cells. Moreover, in cancer cells with centrosome amplification, the CEP215-HSET complex promotes the clustering of extra centrosomes into pseudo-bipolar spindles, thereby ensuring viable cell division. Therefore, stabilization of the centrosome-spindle pole interface by the CEP215-HSET complex could promote survival of cancer cells containing supernumerary centrosomes.
Figures

References
-
- Gonczy P. Towards a molecular architecture of centriole assembly. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 425–435 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Chavali P. L., Peset I. & Gergely F. Centrosomes and mitotic spindle poles: a recent liaison? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 43, 13–18 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Khodjakov A., Cole R. W., Oakley B. R. & Rieder C. L. Centrosome-independent mitotic spindle formation in vertebrates. Curr. Biol. 10, 59–67 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

