A randomized, double-blinded, double-dummy efficacy and safety study of budesonide-formoterol Spiromax® compared to budesonide-formoterol Turbuhaler® in adults and adolescents with persistent asthma
- PMID: 26987997
- PMCID: PMC4794916
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-016-0200-x
A randomized, double-blinded, double-dummy efficacy and safety study of budesonide-formoterol Spiromax® compared to budesonide-formoterol Turbuhaler® in adults and adolescents with persistent asthma
Abstract
Background: Budesonide and formoterol (BF) Spiromax® is a dry powder inhaler designed to deliver BF with maximum ease of use for patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Methods: A phase 3b, 12-week, multicenter, double-blind, double-dummy, randomized, controlled trial in patients (≥12 years) with persistent asthma.
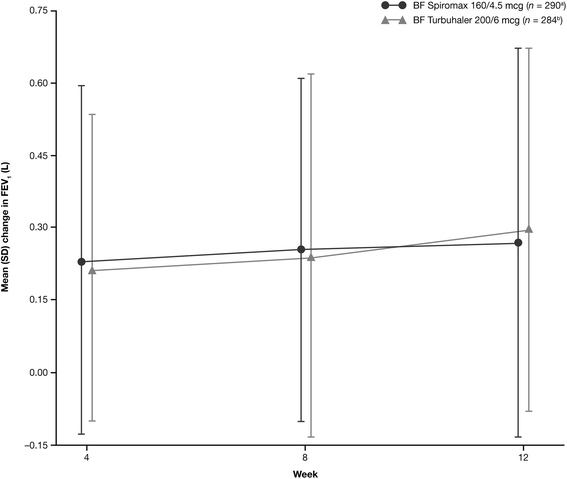
Primary objective: to demonstrate non-inferiority of twice-daily BF Spiromax 160/4.5 mcg to BF Turbuhaler® 200/6 mcg in change from baseline in weekly average of daily trough morning peak expiratory flow (PEF). Secondary endpoints included: Patient Satisfaction and Preference Questionnaire scores, change from baseline in evening PEF, trough forced expiratory volume in one second, percentage of symptom-free and rescue-free 24-hour periods, and safety.
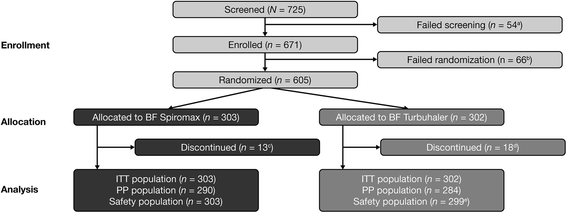
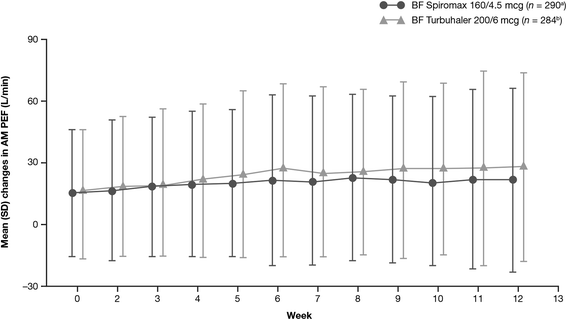
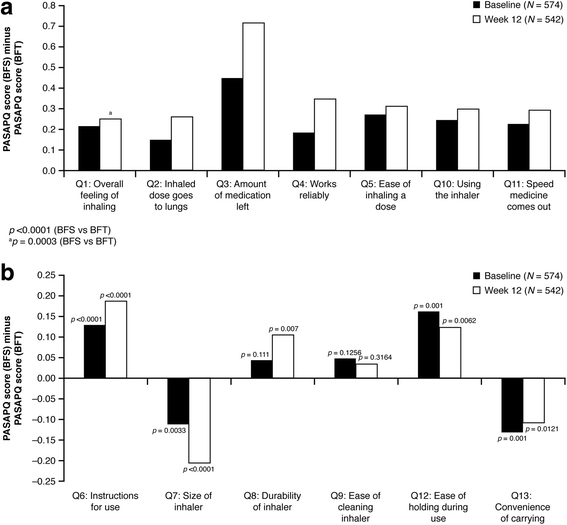
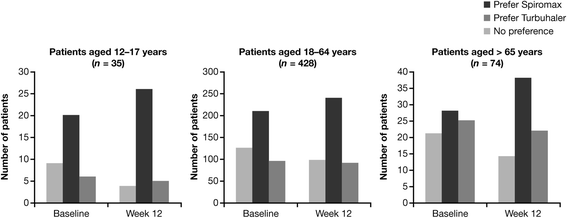
Results: The analysis was based on the per-protocol population (BF Spiromax, n = 290; BF Turbuhaler, n = 284). The least squares mean change from baseline to week 12 in morning PEF was: BF Spiromax, 18.8 L/min and BF Turbuhaler, 21.8 L/min. Non-inferiority of BF Spiromax vs BF Turbuhaler was demonstrated (the lower limit of the 95% two-sided confidence interval was -9.02 L/min, which is greater than -15 L/min [the criteria specified for non-inferiority]). The mean difference in the total performance domains scores for BF Spiromax vs BF Turbuhaler were 0.248 at baseline and 0.353 at week 12 (both, p <0.001), indicating statistical superiority for BF Spiromax. No statistical or numerical differences were recorded in the total convenience domain score between the two devices. Scores for 'device preference' and 'willingness to continue' supported BF Spiromax at baseline and at week 12 (p = 0.0005 vs BF Turbuhaler). No significant between-group differences were observed in the other secondary efficacy endpoints. Both treatments were well tolerated, with no significant differences in adverse events or asthma exacerbations.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates the non-inferiority of BF Spiromax vs BF Turbuhaler in patients (≥12 years) with asthma. More patients preferred the Spiromax device over Turbuhaler for its performance, and were willing to continue therapy with BF Spiromax beyond the 12-week study period.
Trial registration: NCT01803555; February 28, 2013.
Keywords: Asthma; Budesonide; Formoterol; Patient satisfaction and preference questionnaire for inhalation devices; Pulmonary; Safety; Spiromax; Turbuhaler.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of inhaler technique and achievement and maintenance of mastery of budesonide/formoterol Spiromax® compared with budesonide/formoterol Turbuhaler® in adult patients with asthma: the Easy Low Instruction Over Time (ELIOT) study.BMC Pulm Med. 2018 Jun 28;18(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12890-018-0665-x. BMC Pulm Med. 2018. PMID: 29954359 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Budesonide + formoterol delivered via Spiromax® for the management of asthma and COPD: The potential impact on unscheduled healthcare costs of improving inhalation technique compared with Turbuhaler®.Respir Med. 2017 Aug;129:179-188. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2017.06.018. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Respir Med. 2017. PMID: 28732829
-
Fluticasone/formoterol combination therapy versus budesonide/formoterol for the treatment of asthma: a randomized, controlled, non-inferiority trial of efficacy and safety.J Asthma. 2012 Dec;49(10):1060-70. doi: 10.3109/02770903.2012.719253. Epub 2012 Oct 26. J Asthma. 2012. PMID: 23102189 Clinical Trial.
-
Budesonide/formoterol Turbuhaler®: a review of its use in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Drugs. 2012 Feb 12;72(3):395-414. doi: 10.2165/11208460-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22316354 Review.
-
Symbicort: controlling asthma in adults.Respir Med. 2002 Feb;96 Suppl A:S16-22. Respir Med. 2002. PMID: 11858561 Review.
Cited by
-
What to consider before prescribing inhaled medications: a pragmatic approach for evaluating the current inhaler landscape.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2019 Jan-Dec;13:1753466619884532. doi: 10.1177/1753466619884532. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2019. PMID: 31805823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-world effectiveness evaluation of budesonide/formoterol Spiromax for the management of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the UK.BMJ Open. 2018 Oct 27;8(10):e022051. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-022051. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 30368448 Free PMC article.
-
Narrative Review of the Role of Patient-Reported Outcomes and Inhaler Handling Errors in the Control of Asthma and COPD.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2022 Nov;22(11):151-161. doi: 10.1007/s11882-022-01041-2. Epub 2022 Sep 10. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2022. PMID: 36087251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of correct technique and preference for Spiromax®, Easyhaler® and Turbuhaler®: a single-site, single-visit, crossover study in inhaler-naïve adult volunteers.Eur Clin Respir J. 2018 Oct 22;5(1):1529536. doi: 10.1080/20018525.2018.1529536. eCollection 2018. Eur Clin Respir J. 2018. PMID: 30370020 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Dry Powder Inhalers: Key Technical and Patient Preference Attributes.Adv Ther. 2019 Oct;36(10):2547-2557. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-01066-6. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Adv Ther. 2019. PMID: 31478131 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). 2015 update. http://www.ginasthma.org/local/uploads/files/GINA_Report_2015_Aug11.pdf Accessed 7 Mar 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

