Room temperature stable carbetocin for the prevention of postpartum haemorrhage during the third stage of labour in women delivering vaginally: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 26988231
- PMCID: PMC4794812
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1271-y
Room temperature stable carbetocin for the prevention of postpartum haemorrhage during the third stage of labour in women delivering vaginally: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Postpartum haemorrhage (PPH) is the leading cause of maternal mortality in low-income countries and contributes to nearly a quarter of maternal deaths globally. The current available interventions for prevention of postpartum haemorrhage, oxytocin and carbetocin, are limited by their need for refrigeration to maintain potency, as the ability to maintain a cold chain across the drug distribution and storage network is inconsistent, thus restricting their use in countries with the highest burden of maternal mortality. We describe a randomized, double-blind non-inferiority trial comparing a newly developed room temperature stable formulation of carbetocin to the standard intervention (oxytocin) for the prevention of PPH after vaginal birth.
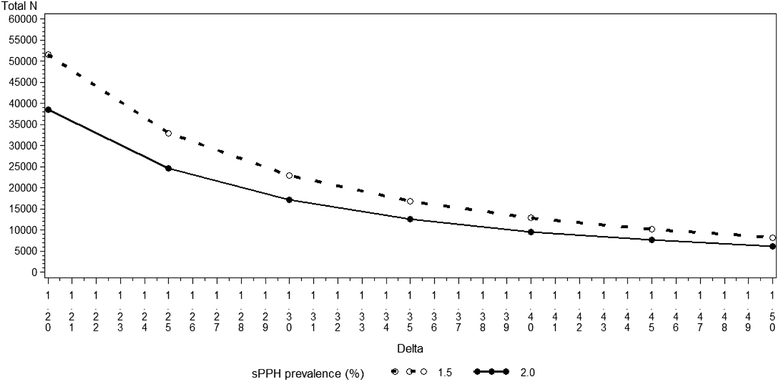
Methods/design: Approximately 30,000 women delivering vaginally will be recruited across 22 centres in 10 countries. The primary objectives are to evaluate the non-inferiority of room temperature stable carbetocin (100 μg intramuscular) versus oxytocin (10 IU intramuscular) in the prevention of PPH and severe PPH after vaginal birth. The primary endpoints are blood loss ≥500 mL or the use of additional uterotonics (composite endpoint required by drug regulatory authorities) and blood loss ≥1,000 mL (WHO requirement). Non-inferiority will be assessed using a two-sided 95 % confidence interval for the relative risk of the above endpoints for room temperature stable carbetocin versus oxytocin. The upper limit of the two-sided 95 % confidence interval for the relative risk for the composite endpoint of blood loss ≥500 mL or the use of additional uterotonics, and for the endpoint of blood loss ≥1,000 mL, will be compared to a non-inferiority margin of 1.16 and 1.23, respectively. If the upper limit is below the corresponding margin, non-inferiority will have been demonstrated. The safety analysis will include all women receiving treatment. Safety and tolerability will be assessed by a review of adverse events, by conducting inferential testing with significance levels for between-group comparisons.
Discussion: If the results of the study show that room temperature stable carbetocin is a safe and effective alternative to oxytocin, this could have a substantial impact on the prevention of postpartum haemorrhage and maternal survival worldwide.
Trial registration: ACTRN12614000870651 (14 August 2014).
Keywords: Non-inferiority trial; Oxytocin; Postpartum haemorrhage; Room temperature stable carbetocin.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Recommendations for the prevention and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2012. - PubMed
-
- Souza JP, Gülmezoglu AM, Vogel J, Carroli G, Lumbiganon P, Qureshi Z, Costa MJ, Fawole B, Mugerwa Y, Nafiou I, Neves I, Wolomby-Molondo JJ, Bang HT, Cheang K, Chuyun K, Jayaratne K, Jayathilaka CA, Mazhar SB, Mori R, Mustafa ML, Pathak LR, Perera D, Rathavy T, Recidoro Z, Roy M, Ruyan P, Shrestha N, Taneepanichsku S, Tien NV, Ganchimeg T, Wehbe M, Yadamsuren B, Yan W, Yunis K, Bataglia V, Cecatti JG, Hernandez-Prado B, Nardin JM, Narváez A, Ortiz-Panozo E, Pérez-Cuevas R, Valladares E, Zavaleta N, Armson A, Crowther C, Hogue C, Lindmark G, Mittal S, Pattinson R, Stanton ME, Campodonico L, Cuesta C, Giordano D, Intarut N, Laopaiboon M, Bahl R, Martines J, Mathai M, Merialdi M, Say L. Moving beyond essential interventions for reduction of maternal mortality (the WHO Multicountry Survey on Maternal and Newborn Health): a cross-sectional study. Lancet. 2013;9879(381):1747–55. - PubMed
-
- Heat-stable oxytocin - Technology opportunity assessment report. PATH, February 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical