Ca2+ is a key factor in α-synuclein-induced neurotoxicity
- PMID: 26989132
- PMCID: PMC4893653
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.180737
Ca2+ is a key factor in α-synuclein-induced neurotoxicity
Abstract
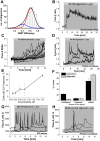
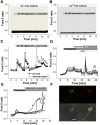
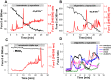
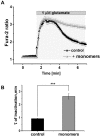
Aggregation of α-synuclein leads to the formation of oligomeric intermediates that can interact with membranes to form pores. However, it is unknown how this leads to cell toxicity in Parkinson's disease. We investigated the species-specific effects of α-synuclein on Ca(2+) signalling in primary neurons and astrocytes using live neuronal imaging and electrophysiology on artificial membranes. We demonstrate that α-synuclein induces an increase in basal intracellular Ca(2+) in its unfolded monomeric state as well as in its oligomeric state. Electrophysiology of artificial membranes demonstrated that α-synuclein monomers induce irregular ionic currents, whereas α-synuclein oligomers induce rare discrete channel formation events. Despite the ability of monomeric α-synuclein to affect Ca(2+) signalling, it is only the oligomeric form of α-synuclein that induces cell death. Oligomer-induced cell death was abolished by the exclusion of extracellular Ca(2+), which prevented the α-synuclein-induced Ca(2+) dysregulation. The findings of this study confirm that α-synuclein interacts with membranes to affect Ca(2+) signalling in a structure-specific manner and the oligomeric β-sheet-rich α-synuclein species ultimately leads to Ca(2+) dysregulation and Ca(2+)-dependent cell death.
Keywords: Ca2+ signalling; Neuronal death; Parkinson's disease; α-Synuclein.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Buttner S., Faes L., Reichelt W. N., Broeskamp F., Habernig L., Benke S., Kourtis N., Ruli D., Carmona-Gutierrez D., Eisenberg T. et al. (2013). The Ca2+/Mn2+ ion-pump PMR1 links elevation of cytosolic Ca(2+) levels to alpha-synuclein toxicity in Parkinson's disease models. Cell Death. Differ. 20, 465-477. 10.1038/cdd.2012.142 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen S. W., Drakulic S., Deas E., Ouberai M., Aprile F. A., Arranz R., Ness S., Roodveldt C., Guilliams T., De-Genst E. J. et al. (2015). Structural characterization of toxic oligomers that are kinetically trapped during alpha-synuclein fibril formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, E1994-E2003. 10.1073/pnas.1421204112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

