Prenatal Exposures to Multiple Thyroid Hormone Disruptors: Effects on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism
- PMID: 26989557
- PMCID: PMC4773558
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/8765049
Prenatal Exposures to Multiple Thyroid Hormone Disruptors: Effects on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism
Abstract
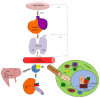
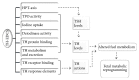
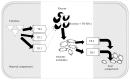
Background. Thyroid hormones (THs) are essential for normal human fetal development and play a major role in the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Delivery of TH to target tissues is dependent on processes including TH synthesis, transport, and metabolism. Thyroid hormone endocrine disruptors (TH-EDCs) are chemical substances that interfere with these processes, potentially leading to adverse pregnancy outcomes. Objectives. This review focuses on the effects of prenatal exposures to combinations of TH-EDCs on fetal and neonatal glucose and lipid metabolism and also discusses the various mechanisms by which TH-EDCs interfere with other hormonal pathways. Methods. We conducted a comprehensive narrative review on the effects of TH-EDCs with particular emphasis on exposure during pregnancy. Discussion. TH imbalance has been linked to many metabolic processes and the effects of TH imbalance are particularly pronounced in early fetal development due to fetal dependence on maternal TH for proper growth and development. The pervasive presence of EDCs in the environment results in ubiquitous exposure to either single or mixtures of EDCs with deleterious effects on metabolism. Conclusions. Further evaluation of combined effects of TH-EDCs on fetal metabolic endpoints could improve advice provided to expectant mothers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on thyroid function and brain development.Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Nov;9(6):579-591. doi: 10.1586/17446651.2014.950227. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 30736196
-
Thyroid Hormone Biomonitoring: A Review on Their Metabolism and Machine-Learning Based Analysis on Effects of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals.Environ Health (Wash). 2024 Mar 4;2(6):350-372. doi: 10.1021/envhealth.3c00184. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. Environ Health (Wash). 2024. PMID: 39473465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocrine Disruptors and Thyroid Health.Endocr Pract. 2024 Feb;30(2):172-176. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2023.11.002. Epub 2023 Nov 11. Endocr Pract. 2024. PMID: 37956907 Review.
-
Environmental chemicals targeting thyroid.Hormones (Athens). 2010 Jan-Mar;9(1):28-40. doi: 10.14310/horm.2002.1250. Hormones (Athens). 2010. PMID: 20363719 Review.
-
Transcriptomics investigation of thyroid hormone disruption in the olfactory system of the Rana [Lithobates] catesbeiana tadpole.Aquat Toxicol. 2018 Sep;202:46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.06.015. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Aquat Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30007154
Cited by
-
Intrauterine exposure to low-dose DBP in the mice induces obesity in offspring via suppression of UCP1 mediated ER stress.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 1;10(1):16360. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73477-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33004990 Free PMC article.
-
A pathway level analysis of PFAS exposure and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus.Environ Health. 2021 May 22;20(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12940-021-00740-z. Environ Health. 2021. PMID: 34022907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Emerging Role of micro-RNA in the Effect of the Endocrine Disruptors.Front Neurosci. 2016 Jun 30;10:318. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00318. eCollection 2016. Front Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27445682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uncontrolled Thyroid during Pregnancy Alters the Circulative and Exerted Metabolome.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 12;23(8):4248. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084248. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457066 Free PMC article.
-
Differential susceptibility to endocrine disruptor-induced epimutagenesis.Environ Epigenet. 2020 Dec 8;6(1):dvaa016. doi: 10.1093/eep/dvaa016. eCollection 2020. Environ Epigenet. 2020. PMID: 33324495 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Calvo R., Obregon M. J., Ruiz de Ona C., Escobar del Rey F., Morreale de Escobar G. Congenital hypothyroidism, as studied in rats. Crucial role of maternal thyroxine but not of 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine in the protection of the fetal brain. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1990;86(3):889–899. doi: 10.1172/jci114790. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Préau L., Fini J. B., Morvan-Dubois G., Demeneix B. Thyroid hormone signaling during early neurogenesis and its significance as a vulnerable window for endocrine disruption. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)—Gene Regulatory Mechanisms. 2015;1849(2):112–121. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.06.015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

