Re-starting smoking in the postpartum period after receiving a smoking cessation intervention: a systematic review
- PMID: 26990248
- PMCID: PMC6680353
- DOI: 10.1111/add.13309
Re-starting smoking in the postpartum period after receiving a smoking cessation intervention: a systematic review
Abstract
Aims: In pregnant smoking cessation trial participants, to estimate (1) among women abstinent at the end of pregnancy, the proportion who re-start smoking at time-points afterwards (primary analysis) and (2) among all trial participants, the proportion smoking at the end of pregnancy and at selected time-points during the postpartum period (secondary analysis).
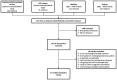
Methods: Trials identified from two Cochrane reviews plus searches of Medline and EMBASE. Twenty-seven trials were included. The included trials were randomized or quasi-randomized trials of within-pregnancy cessation interventions given to smokers who reported abstinence both at end of pregnancy and at one or more defined time-points after birth. Outcomes were validated biochemically and self-reported continuous abstinence from smoking and 7-day point prevalence abstinence. The primary random-effects meta-analysis used longitudinal data to estimate mean pooled proportions of re-starting smoking; a secondary analysis used cross-sectional data to estimate the mean proportions smoking at different postpartum time-points. Subgroup analyses were performed on biochemically validated abstinence.
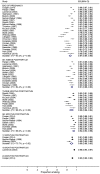
Results: The pooled mean proportion re-starting at 6 months postpartum was 43% [95% confidence interval (CI) = 16-72%, I(2) = 96.7%] (11 trials, 571 abstinent women). The pooled mean proportion smoking at the end of pregnancy was 87% (95% CI = 84-90%, I(2) = 93.2%) and 94% (95% CI = 92-96%, I(2) = 88%) at 6 months postpartum (23 trials, 9262 trial participants). Findings were similar when using biochemically validated abstinence.
Conclusions: In clinical trials of smoking cessation interventions during pregnancy only 13% are abstinent at term. Of these, 43% re-start by 6 months postpartum.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; postpartum period; pregnancy; randomized controlled trial; re-starting smoking; smoking; smoking cessation; smoking cessation interventions; systematic review; tobacco.
© 2016 The Authors. Addiction published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures

Comment in
-
The importance of permanent cessation for pregnant smokers.Addiction. 2016 Jun;111(6):991-2. doi: 10.1111/add.13325. Addiction. 2016. PMID: 27157901 No abstract available.
-
Failure to change or failure to sustain: pregnancy smoking and postpartum abstinence.Addiction. 2016 Jun;111(6):992-3. doi: 10.1111/add.13393. Addiction. 2016. PMID: 27157902 No abstract available.
References
-
- Samet J. M., Yoon S. Y., World Health Organization . Gender, Women and the Tobacco Epidemic. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010.
-
- Godfrey C., Pickett K. E., Parrott S., Mdege N. D., Eapen D. Estimating the Costs to the NHS of Smoking in Pregnancy for Pregnant Women and Infants. York: Public Health Research Consortium, University of York, 2010.
-
- European Medicines Agency . Guideline on the Development of Medicinal Products for the Treatment of Smoking. London: European Medicines Agency; 2008.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Trends in Smoking Before, During, and After Pregnancy—Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System, United States, 40 Sites, 2000–2010. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

