Hemoglobin Decrease with Iron Deficiency Induced by Daclatasvir plus Asunaprevir Combination Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 1b
- PMID: 26990758
- PMCID: PMC4798293
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151238
Hemoglobin Decrease with Iron Deficiency Induced by Daclatasvir plus Asunaprevir Combination Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 1b
Abstract
Background: Decreased hemoglobin (Hb) level has been supposed to be a relatively rare side effect of a combination therapy against hepatitis C virus that consists of the NS5A inhibitor daclatasvir (DCV) and the NS3/4A protease inhibitor asunaprevir (ASV).
Methods: The study was conducted in 75 patients with genotype 1b chronic hepatitis C virus infection who had started combination therapy with DCV and ASV at St. Marianna University School of Medicine Hospital between September 2014 and December 2014.
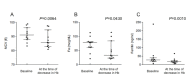
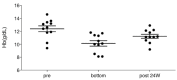
Results: Among the patients examined, decreased Hb level by ≥1.5 g/dL from the values at treatment initiation was observed in 11 individuals. This was accompanied by decreased mean corpuscular volume, and iron and ferritin levels.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that the mechanism of the phenomenon is caused by iron deficiency. The underlying mechanism and clinical impacts will need to be further examined.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Vallet-Pichard A, Mallet V, Nalpas B, Verkarre V, Nalpas A, Dhalluin-Venier V, et al. FIB-4: an inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection. comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology. 2007; 46: 32–36. - PubMed
-
- Short MW, Domagalski JE. Hemoglobin decrease: evaluation and management. Am Fam Physician. 2013; 87: 98–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

