Impact of patient characteristics on the pharmacokinetics of corifollitropin alfa during controlled ovarian stimulation
- PMID: 26991902
- PMCID: PMC4917789
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.12939
Impact of patient characteristics on the pharmacokinetics of corifollitropin alfa during controlled ovarian stimulation
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the present study was to characterize the pharmacokinetic profile of corifollitropin alfa and examine the relationships between dose, intrinsic factors [body weight, body mass index (BMI), age and race] and corifollitropin alfa pharmacokinetics.
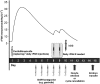
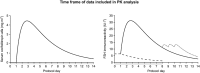
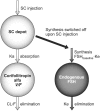
Methods: Data from five phase II and III clinical trials of corifollitropin alfa were evaluated. All subjects included in the analysis received 60 - 180 μg corifollitropin alfa for controlled ovarian stimulation in a gonadotrophin-releasing hormone antagonist protocol followed by daily recombinant follicle stimulating hormone (rFSH) from day 8 onwards. Serum corifollitropin alfa levels (across the entire range of treatment) and total follicle stimulating hormone immunoreactivity levels (up to the start of rFSH treatment) were indicators of drug exposure. The analyses were performed using a nonlinear mixed-effects modelling approach.
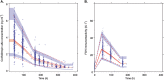
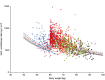
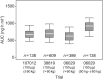
Results: A total of 2630 subjects were treated with corifollitropin alfa, and 2557 subjects were evaluable for analysis. Body weight, BMI and race (Asian and Black vs. Caucasian) were significant determinants of corifollitropin alfa exposure. Dose-normalized corifollitropin alfa exposure was ~89% higher in women with a body weight of 50 kg vs. 90 kg (in subjects with a similar BMI of 24 kg m(-2) ); 14% higher in women with a BMI of 18 kg m(-2) vs. 32 kg m(-2) (provided they were of similar body weight); and ~15.7% lower in Asian subjects and 13% higher in Black subjects vs. Caucasian subjects.
Conclusions: Body weight was the major determinant of corifollitropin alfa exposure; BMI and race (Asian and Black) were also determinants but to a lesser extent and without associated effects on clinical outcomes. Corifollitropin alfa dose adjustment is indicated, based on body weight but not for BMI or race. These recommendations are consistent with the product label.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00598208 NCT00702845 NCT00696800 NCT00696878 NCT01144416.
Keywords: age; controlled ovarian stimulation; corifollitropin alfa; population pharmacokinetics; race; weight.
© 2016 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Fauser BC, Mannaerts BM, Devroey P, Leader A, Boime I, Baird DT. Advances in recombinant DNA technology: corifollitropin alfa, a hybrid molecule with sustained follicle‐stimulating activity and reduced injection frequency. Hum Reprod Update 2009; 15: 309–21. - PubMed
-
- European Medicines Agency . Elonva (corifollitropin alfa): summary of product characteristics. 2011. Available at http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_‐_Product_Info... (last accessed 15 April 2016).
-
- Corifollitropin alfa Ensure Study Group . Corifollitropin alfa for ovarian stimulation in IVF: a randomized trial in lower‐body‐weight women. Reprod Biomed Online 2010; 21: 66–76. - PubMed
-
- Boostanfar R, Shapiro B, Levy M, Rosenwaks Z, Witjes H, Stegmann BJ, et al Large, comparative, randomized double‐blind trial confirming noninferiority of pregnancy rates for corifollitropin alfa compared with recombinant follicle‐stimulating hormone in a gonadotropin‐releasing hormone antagonist controlled ovarian stimulation protocol in older patients undergoing in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril 2015; 104: 94–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

