Clonal Structure and Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Strains from Invasive Infections in Paediatric Patients from South Poland: Association between Age, spa Types, Clonal Complexes, and Genetic Markers
- PMID: 26992009
- PMCID: PMC4798296
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151937
Clonal Structure and Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Strains from Invasive Infections in Paediatric Patients from South Poland: Association between Age, spa Types, Clonal Complexes, and Genetic Markers
Erratum in
-
Correction: Clonal Structure and Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Strains from Invasive Infections in Paediatric Patients from South Poland: Association between Age, spa Types, Clonal Complexes, and Genetic Markers.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 21;11(4):e0154485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154485. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27100992 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
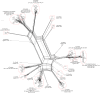
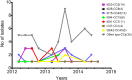
The aim of current study was to examine clonal structure and genetic profile of invasive Staphylococcus aureus isolates recovered from infants and children treated at the Jagiellonian University Children's Hospital of Krakow, Poland. The 107 invasive S. aureus isolates, collected between February 2012 and August 2014, were analysed retrospectively. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing, spa typing and DNA microarray analysis were performed to determine clonal distribution, diversity and gene content in regard to patients characteristics. In total, 107 isolates were recovered from 88 patients with clinical symptoms of invasive bacterial infection. The final set of 92 non-duplicate samples included 38 MRSA isolates. Additionally, a set of 54 S. aureus isolates collected during epidemiological screening was genotyped and analysed. There were 72 healthcare-associated (HCA) and 20 community-onset (CO) infection events caused by 33 and 5 MRSA isolates, respectively. The majority of isolates were affiliated with the major European clonal complexes CC5 (t003, spa-CC 002), CC45 (spa-CC 015), CC7 or CC15 (t084, t091, spa-CC 084). Two epidemic clones (CC5-MRSA-II or CC45-MRSA-IV) dominated among MRSA isolates, while MSSA population contained 15 different CCs. The epidemiological screening isolates belonged to similar genetic lineages as those collected from invasive infection cases. The HCA infection events, spa types t003, t2642 or CC5 were significantly associated with infections occurring in neonates and children under 5 years of age. Moreover, carriage of several genetic markers, including erm(A), sea (N315), egc-cluster, chp was significantly higher in isolates obtained from children in this age group. The spa types t091 and t008 were underrepresented among patients aged 5 years or younger, whereas spa type t008, CC8 and presence of splE was associated with infection in children aged 10 years or older. The HCA-MRSA strains were most frequently found in children under 5 years, although the majority of invasive infections was associated with MSSA strains. Moreover, an association between age group of children from the study population and a specific strain genotype (spa type, clonal complex or genetic content) was observed among the patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Infectivity-resistotype-genotype clustering of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in the Central Blacksea Region of Turkey].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2014 Jan;48(1):14-27. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2014. PMID: 24506712 Turkish.
-
Epidemiology and molecular characteristics of community-associated methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus from skin/soft tissue infections in a children's hospital in Beijing, China.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010 May;67(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2009.12.006. Epub 2010 Mar 12. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20227225
-
Presence of egc-positive major clones ST 45, 30 and 22 among methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible oral Staphylococcus aureus strains.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 3;10(1):18889. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76009-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33144661 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus native arthritis over 10 years.Med Mal Infect. 2020 May;50(3):257-262. doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2020.01.012. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Med Mal Infect. 2020. PMID: 32057526 Review.
-
Staphylococcus aureus clones causing osteomyelitis: a literature review (2000-2020).J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2021 Sep;26:29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2021.03.030. Epub 2021 May 6. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2021. PMID: 33965630 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial resistance profile of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in children reported from the ISPED surveillance of bacterial resistance, 2016-2021.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jan 19;13:1102779. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1102779. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36743309 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, Genetic Diversity, and Temporary Shifts of Inducible Clindamycin Resistance Staphylococcus aureus Clones in Tehran, Iran: A Molecular-Epidemiological Analysis From 2013 to 2018.Front Microbiol. 2020 Apr 30;11:663. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00663. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32425898 Free PMC article.
-
New Threats from an Old Foe: Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infections in Neonates.Neonatology. 2018;114(2):127-134. doi: 10.1159/000488582. Epub 2018 May 25. Neonatology. 2018. PMID: 29804104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolated from humans and pets - a comparison of drug resistance and risk factors associated with colonisation.J Vet Res. 2025 Jun 18;69(2):199-211. doi: 10.2478/jvetres-2025-0036. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40568467 Free PMC article.
-
The antimicrobial activity of cethromycin against Staphylococcus aureus and compared with erythromycin and telithromycin.BMC Microbiol. 2023 Apr 20;23(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02858-1. BMC Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37081393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Romaniszyn D, Różańska A, Wójkowska-Mach J, Chmielarczyk A, Pobiega M, Adamski P, et al. Epidemiology, antibiotic consumption and molecular characterisation of Staphylococcus aureus infections—data from the Polish Neonatology Surveillance Network, 2009–2012. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15: 169 10.1186/s12879-015-0890-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wójkowska-Mach J, Gulczyńska E, Nowiczewski M, Borszewska-Kornacka M, Domańska J, Merritt TA, et al. Late-onset bloodstream infections of Very-Low-Birth-Weight infants: data from the Polish Neonatology Surveillance Network in 2009–2011. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14: 339 10.1186/1471-2334-14-339 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

