Non-ionizing real-time ultrasonography in implant and oral surgery: A feasibility study
- PMID: 26992276
- PMCID: PMC11992668
- DOI: 10.1111/clr.12805
Non-ionizing real-time ultrasonography in implant and oral surgery: A feasibility study
Abstract
Purpose: Ultrasound imaging has potential to complement radiographic imaging modalities in implant and oral surgery given that it is non-ionizing and provides instantaneous images of anatomical structures. For application in oral and dental imaging, its qualities are dependent on its ability to accurately capture these complex structures. Therefore, the aim of this feasibility study was to investigate ultrasound to image soft tissue, hard tissue surface topography and specific vital structures.
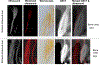
Material and methods: A clinical ultrasound scanner, paired with two 14-MHz transducers of different sizes (one for extraoral and the other for intraoral scans), was used to scan the following structures on a fresh cadaver: (i) the facial bone surface and soft tissue of maxillary anterior teeth, (ii) the greater palatine foramen; (iii) the mental foramen and (iv) the lingual nerve. Multiple measurements relevant to these structures were made on the ultrasound images and compared to those on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans and/or direct measurements.
Results: Ultrasound imaging could delineate hard tissue surfaces, including enamel, root dentin and bone as well as soft tissue with high resolution (110 μm wavelength). The greater palatine foramen, mental foramen and lingual nerve were clearly shown in ultrasound images. Merging ultrasound and CBCT images demonstrated overall spatial accuracy of ultrasound images, which was corroborated by data gathered from direct measurements.
Conclusion: For the first time, this study provides proof-of-concept evidence that ultrasound can be a real-time and non-invasive alternative for the evaluation of oral and dental anatomical structures relevant for implant and oral surgery.
Keywords: alveolar ridge; anatomy; bone regeneration; cone-beam computed tomography; dental implants; ultrasonography.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Aggarwal V, Logani A. & Shah N. (2008) The evaluation of computed tomography scans and ultrasounds in the differential diagnosis of periapical lesions. Journal of Endodontics 34: 1312–1315. - PubMed
-
- Barratt DC, Penney GP, Chan CS, Slomczykowski M, Carter TJ, Edwards PJ & Hawkes DJ (2006) Self-calibrating 3d-ultrasound-based bone registration for minimally invasive orthopedic surgery. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 25: 312–323. - PubMed
-
- Bozkurt FO, Tagtekin DA, Hayran O, Stookey GK & Yanikoglu FC (2005) Accuracy of ultrasound measurement of progressive change in occlusal enamel thickness. Oral Surgery Oral Medicine Oral Pathology Oral Radiology and Endodontology 99: 101–105. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

