Anterior spinal fixation for recollapse of cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty
- PMID: 26994051
- PMCID: PMC4800242
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2016-214510
Anterior spinal fixation for recollapse of cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty
Abstract
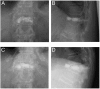
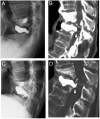
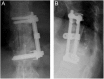
Although recollapse after percutaneous vertebroplasty (PV) is a serious complication that needs salvage surgery, there is no consensus regarding the best operative treatment for this failure. We present cases of 3 patients, diagnosed as having thoracic osteoporotic vertebral fractures, who had undergone PV at other institutes. Within less than half a year, recollapse occurred at the cemented vertebrae in all 3 patients, and we conducted anterior spinal fixation (ASF) on them. In all cases, ASF relieved the patient's severe low back pain, and there was no recurrence of symptoms during the follow-up period of 6 years, on average. ASF is the optimal salvage procedure, since it allows for the direct decompression of nerve tissue with reconstruction of the collapsed spinal column, and preservation of the ligaments and muscles that stabilise the posterior spine. Surgeons who perform PV need to be able to assess this failure early and to perform spinal fixation.
2016 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Recollapse of previous vertebral compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty.Osteoporos Int. 2009 Mar;20(3):473-80. doi: 10.1007/s00198-008-0682-3. Epub 2008 Jul 18. Osteoporos Int. 2009. PMID: 18636218
-
Anterior thoracolumbar reconstruction surgery for late collapse following vertebroplasty: report of three cases.J Med Invest. 2011 Feb;58(1-2):148-53. doi: 10.2152/jmi.58.148. J Med Invest. 2011. PMID: 21372500
-
[Effectiveness of long segment fixation combined with vertebroplasty for severe osteoporotic thoracolumbar compressive fractures].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Nov;27(11):1331-7. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24501892 Chinese.
-
Current status of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fracture.Chang Gung Med J. 2011 Jul-Aug;34(4):352-9. Chang Gung Med J. 2011. PMID: 21880189 Review.
-
Giant cell tumor of the eleventh thoracic vertebra in a pediatric patient: an interesting case report and comprehensive literature review.Childs Nerv Syst. 2019 Mar;35(3):553-557. doi: 10.1007/s00381-018-3980-x. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Childs Nerv Syst. 2019. PMID: 30259086 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive risk factors for recollapse of cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty: A meta-analysis.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Apr 26;9(12):2778-2790. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i12.2778. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 33969060 Free PMC article.
-
Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery for Re-Collapse of Vertebrae after Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation (PVA).Spine Surg Relat Res. 2020 Jul 10;5(1):28-33. doi: 10.22603/ssrr.2020-0009. eCollection 2021. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2020. PMID: 33575492 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of and Risk Factors for Neurological Deficits Associated With Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation.Global Spine J. 2025 Apr 9:21925682251333412. doi: 10.1177/21925682251333412. Online ahead of print. Global Spine J. 2025. PMID: 40205827 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy analysis of percutaneous pedicle screw fixation combined with percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with kyphosis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Feb 17;15(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-1583-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32066480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P et al. . [Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty]. Neurochirurgie 1987;33:166–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
