RNA Imaging with Dimeric Broccoli in Live Bacterial and Mammalian Cells
- PMID: 26995352
- PMCID: PMC4829638
- DOI: 10.1002/9780470559277.ch150174
RNA Imaging with Dimeric Broccoli in Live Bacterial and Mammalian Cells
Abstract
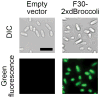
RNA spatial dynamics play a crucial role in cell physiology, and thus the ability to monitor RNA localization in live cells can provide insight into important biological problems. This unit focuses on imaging RNAs using an RNA mimic of GFP. This approach relies on an RNA aptamer called dimeric Broccoli, which binds to and switches on the fluorescence of DFHBI, a small molecule mimicking the fluorophore in GFP. Dimeric Broccoli is tagged to heterologously expressed RNAs and, upon DFHBI binding, the fluorescent signal of dimeric Broccoli reports the transcript's localization in cells. This protocol describes the process of validating the fluorescence of dimeric Broccoli--labeled transcripts in vitro and in cells, flow cytometry analysis to determine overall fluorescence levels in cells, and fluorescence imaging in bacterial and mammalian cells. Overall, the protocol should be useful for researchers seeking to image high-abundance RNAs, such as those transcribed off the T7 promoter in bacteria or off Pol III--dependent promoters in mammalian cells.
Keywords: RNA aptamer; RNA imaging; aptamer expression; fluorescence microscopy.
Copyright © 2016 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Figures


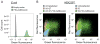

References
-
- Bao G, Tsourkas A, Santangelo PJ. Engineering nanostructured probes for sensitive intracellular gene detection. Mech Chem Biosyst. 2004;1:23–36. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand E, Chartrand P, Schaefer M, Shenoy SM, Singer RH, Long RM. Localization of ASH1 mRNA particles in living yeast. Molecular Cell. 1998;2:437–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

