Unmasking Latent Inhibitory Connections in Human Cortex to Reveal Dormant Cortical Memories
- PMID: 26996082
- PMCID: PMC4826438
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.02.031
Unmasking Latent Inhibitory Connections in Human Cortex to Reveal Dormant Cortical Memories
Abstract
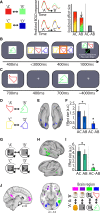
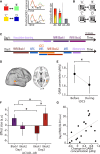
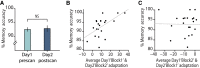
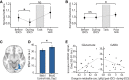
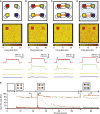
Balance of cortical excitation and inhibition (EI) is thought to be disrupted in several neuropsychiatric conditions, yet it is not clear how it is maintained in the healthy human brain. When EI balance is disturbed during learning and memory in animal models, it can be restabilized via formation of inhibitory replicas of newly formed excitatory connections. Here we assess evidence for such selective inhibitory rebalancing in humans. Using fMRI repetition suppression we measure newly formed cortical associations in the human brain. We show that expression of these associations reduces over time despite persistence in behavior, consistent with inhibitory rebalancing. To test this, we modulated excitation/inhibition balance with transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). Using ultra-high-field (7T) MRI and spectroscopy, we show that reducing GABA allows cortical associations to be re-expressed. This suggests that in humans associative memories are stored in balanced excitatory-inhibitory ensembles that lie dormant unless latent inhibitory connections are unmasked.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
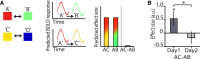
References
-
- Bindman L.J., Lippold O.C., Redfearn J.W. Long-lasting changes in the level of the electrical activity of the cerebral cortex produced bypolarizing currents. Nature. 1962;196:584–585. - PubMed
-
- Brink W.M., Webb A.G. High permittivity pads reduce specific absorption rate, improve B1 homogeneity, and increase contrast-to-noise ratio for functional cardiac MRI at 3 T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014;71:1632–1640. - PubMed
-
- Chagnac-Amitai Y., Connors B.W. Horizontal spread of synchronized activity in neocortex and its control by GABA-mediated inhibition. J. Neurophysiol. 1989;61:747–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

