Autonomous pump against concentration gradient
- PMID: 26996204
- PMCID: PMC4800498
- DOI: 10.1038/srep23414
Autonomous pump against concentration gradient
Abstract
Using non-equilibrium molecular dynamics and Monte Carlo methods, we have studied the molecular transport in asymmetric nanochannels. The efficiency of the molecular pump depends on the angle and apertures of the asymmetric channel, the environmental temperature and average concentration of the particles. The pumping effect can be explained as the competition between the molecular force field and the thermal disturbance. Our results provide a green approach for pumping fluid particles against the concentration gradient through asymmetric nanoscale thin films without any external forces. It indicates that pumping vacuum can be a spontaneous process.
Figures


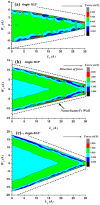


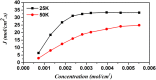
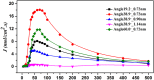

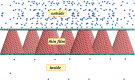
Similar articles
-
A channel Brownian pump powered by an unbiased external force.J Chem Phys. 2008 Jan 14;128(2):024706. doi: 10.1063/1.2813420. J Chem Phys. 2008. PMID: 18205465
-
Bioinspired artificial single ion pump.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Oct 30;135(43):16102-10. doi: 10.1021/ja4037669. Epub 2013 Jul 3. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23773031
-
Study on the Pumping Performance and Structure Parameters Optimization of High-Speed Small Compound Molecular Pump.Micromachines (Basel). 2024 May 29;15(6):717. doi: 10.3390/mi15060717. Micromachines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38930687 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Synthesis of Nonequilibrium Systems.ACS Nano. 2015 Sep 22;9(9):8672-88. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b03809. Epub 2015 Aug 17. ACS Nano. 2015. PMID: 26222543 Review.
-
A review of thermal response test analysis using pumping test concepts.Ground Water. 2011 Nov-Dec;49(6):932-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2010.00791.x. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Ground Water. 2011. PMID: 21306358 Review.
References
-
- Ge M. & Sattler K. Observation of fullerene cones. Chem. Phys. Lett., 220, 192–196 (1994).
-
- Krishnan A. et al. Graphitic cones and the nucleation of curved carbon surfaces. Nature 388, 451–456 (1997).
-
- Charlier J. C. & Rignanese G. M. Electronic structure of carbon nanocones. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5970–5973 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Yang N., Zhang G. & Li B. W. Carbon nanocone: a promising thermal rectifier. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 243111 (2008).
-
- Dimitrakakis G. K., Tylianakis E. & Froudakis G. E. Pillared graphene: a new 3-D network nanostructure for enhanced hydrogen storage. Nano Lett., 8, 3166–3170 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

