Benchmarking the scientific output of industrial wastewater research in Arab world by utilizing bibliometric techniques
- PMID: 26996912
- PMCID: PMC4871912
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-016-6434-6
Benchmarking the scientific output of industrial wastewater research in Arab world by utilizing bibliometric techniques
Abstract
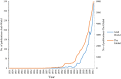
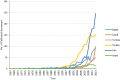
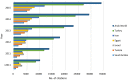
Rapid population growth, worsening of the climate, and severity of freshwater scarcity are global challenges. In Arab world countries, where water resources are becoming increasingly scarce, the recycling of industrial wastewater could improve the efficiency of freshwater use. The benchmarking of scientific output of industrial wastewater research in the Arab world is an initiative that could support in shaping up and improving future research activities. This study assesses the scientific output of industrial wastewater research in the Arab world. A total of 2032 documents related to industrial wastewater were retrieved from 152 journals indexed in the Scopus databases; this represents 3.6 % of the global research output. The h-index of the retrieved documents was 70. The total number of citations, at the time of data analysis, was 34,296 with an average citation of 16.88 per document. Egypt, with a total publications of 655 (32.2 %), was ranked the first among the Arab countries followed by Saudi Arabia 300 (14.7 %) and Tunisia 297 (14.6 %). Egypt also had the highest h-index, assumed with Saudi Arabia, the first place in collaboration with other countries. Seven hundred fifteen (35.2 %) documents with 66 countries in Arab/non-Arab country collaborations were identified. Arab researchers collaborated mostly with researchers from France 239 (11.7 %), followed by the USA 127 (6.2 %). The top active journal was Desalination 126 (6.2 %), and the most productive institution was the National Research Center, Egypt 169 (8.3 %), followed by the King Abdul-Aziz University, Saudi Arabia 75 (3.7 %). Environmental Science was the most prevalent field of interest 930 (45.8 %). Despite the promising indicators, there is a need to close the gap in research between the Arab world and the other nations. Optimizing the investments and developing regional experiences are key factors to promote the scientific research.
Keywords: Arab world; Benchmarking; Bibliometrics; Industrial wastewater; Scopus; h-index.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mapping of climate change research in the Arab world: a bibliometric analysis.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jan;27(3):3523-3540. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07100-y. Epub 2019 Dec 21. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31865588
-
Mapping environmental impact assessment research landscapes in the Arab world using visualization and bibliometric techniques.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 May;28(17):22179-22202. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-13696-x. Epub 2021 Apr 4. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33813693
-
Contribution of Arab countries to breast cancer research: comparison with non-Arab Middle Eastern countries.BMC Womens Health. 2015;15:25. doi: 10.1186/s12905-015-0184-3. Epub 2015 Mar 14. BMC Womens Health. 2015. PMID: 25783656 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of Saudi Arabia to regional and global publications on COVID-19-related research: A bibliometric and visualization analysis.J Infect Public Health. 2022 Jul;15(7):709-719. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2022.05.013. Epub 2022 May 27. J Infect Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35667303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Scopus-based examination of tobacco use publications in Middle Eastern Arab countries during the period 2003-2012.Harm Reduct J. 2014 May 1;11:14. doi: 10.1186/1477-7517-11-14. Harm Reduct J. 2014. PMID: 24885706 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping of climate change research in the Arab world: a bibliometric analysis.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jan;27(3):3523-3540. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07100-y. Epub 2019 Dec 21. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31865588
-
Contribution of Arab countries to pharmaceutical wastewater literature: a bibliometric and comparative analysis of research output.Ann Occup Environ Med. 2016 Jul 3;28:28. doi: 10.1186/s40557-016-0117-0. eCollection 2016. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2016. PMID: 27382475 Free PMC article.
-
Benchmarking the scientific research on wastewater-energy nexus by using bibliometric analysis.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Dec;24(35):27613-27630. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0696-5. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 29134520
-
The way forward confronting eco-environmental challenges during land-use practices: a bibliometric analysis.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Oct;25(28):28296-28311. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2866-5. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30083895
References
-
- Al-Ghasham T, Clark B, Al-Saud AA, Al-Hajji M, Al-Muaibid J, Gauthier C. Industrial wastewater treatment for reuse, assessment study in a Saudi Aramco facility. Saudi Aramco J Technol. 2005;7:52–60.
-
- Alshayea A. Scientific research in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: potential for excellence and indicators of underdevelopment. High Educ Stud. 2013;3:5539.
-
- Al-Zubari WK. Towards the establishment of a total water cycle management and re-use program in the GCC countries. Desalination. 1998;120:3–14. doi: 10.1016/S0011-9164(98)00196-9. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

