Historical Records of Mercury Stable Isotopes in Sediments of Tibetan Lakes
- PMID: 26996936
- PMCID: PMC4800404
- DOI: 10.1038/srep23332
Historical Records of Mercury Stable Isotopes in Sediments of Tibetan Lakes
Abstract
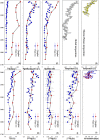
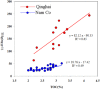
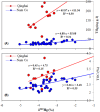
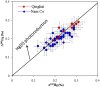
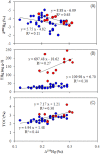
The Tibetan Plateau (TP), known as the "Third Pole", is a critical zone for atmospheric mercury (Hg) deposition. Increasing anthropogenic activities in the globe leads to environmental changes, which may affect the loading, transport and deposition of Hg in the environment. However, the deposition history and geochemical cycling of Hg in the TP is still uncertain. Our records of Hg and Hg isotopes in sediment profiles of the two largest lakes in the TP, Lake Qinghai and Nam Co, show increased Hg influx since last century, with the maximum Hg influx enrichment ratios of 5.4 and 3.5 in Lake Qinghai and Nam Co, respectively. Shifts in negative δ (202)Hg in Lake Qinghai (-4.55 to -3.15‰) and Nam Co (-5.04 to -2.16‰) indicate increased atmospheric Hg deposition through rainfall, vegetation and runoff of soils. Mass independent fractionation of both even-Hg (∆ (200)Hg: +0.05 to +0.10‰) and odd-Hg (∆ (199)Hg: +0.12 to +0.31‰) isotopes were observed. Positive Δ (200)Hg suggest high proportion of precipitation-derived Hg in the TP, whereas the positive Δ (199)Hg results from Hg(II) photo-reduction. Both lakes show increasing Δ (199)Hg since the 1900 s, and we conclude that with the decrease of ice duration, Hg(II) photo-reduction may have been accelerated in these TP lakes.
Figures

References
-
- Yang R., Zhang S., Li A. et al. Altitudinal and spatial signature of persistent organic pollutants in soil, lichen, conifer needles, and bark of the southeast Tibetan Plateau: Implications for sources and environmental cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 12736–12743 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Swartzendruber P. C. et al. Observations of reactive gaseous mercury in the free troposphere at the Mount Bachelor Observatory. J. Geophys. Res. 111, 10.1029/2006JD007415 (2006). - DOI
-
- Loewen M. et al. Atmospheric transport of mercury to the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41, 7632–7638 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Yang H. D. et al. Historical reconstruction of mercury pollution across the Tibetan Plateau using lake sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 2918–2924 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

