Acoustic Injectors for Drop-On-Demand Serial Femtosecond Crystallography
- PMID: 26996959
- PMCID: PMC4920001
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2016.02.007
Acoustic Injectors for Drop-On-Demand Serial Femtosecond Crystallography
Abstract
X-ray free-electron lasers (XFELs) provide very intense X-ray pulses suitable for macromolecular crystallography. Each X-ray pulse typically lasts for tens of femtoseconds and the interval between pulses is many orders of magnitude longer. Here we describe two novel acoustic injection systems that use focused sound waves to eject picoliter to nanoliter crystal-containing droplets out of microplates and into the X-ray pulse from which diffraction data are collected. The on-demand droplet delivery is synchronized to the XFEL pulse scheme, resulting in X-ray pulses intersecting up to 88% of the droplets. We tested several types of samples in a range of crystallization conditions, wherein the overall crystal hit ratio (e.g., fraction of images with observable diffraction patterns) is a function of the microcrystal slurry concentration. We report crystal structures from lysozyme, thermolysin, and stachydrine demethylase (Stc2). Additional samples were screened to demonstrate that these methods can be applied to rare samples.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
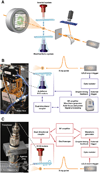
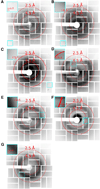
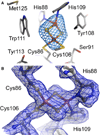
Comment in
-
Acoustic Injectors Meet X-Ray Free-Electron Lasers.Structure. 2016 Apr 5;24(4):500-501. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2016.03.014. Structure. 2016. PMID: 27050686
References
-
- Aerni H-R, Cornett DS, Caprioli RM. Automated acoustic matrix deposition for MALDI sample preparation. Anal. Chem. 2005;78:827–834. - PubMed
-
- Barends TRM, Foucar L, Botha S, Doak RB, Shoeman RL, Nass K, Koglin JE, Williams GJ, Boutet S, Messerschmidt M, et al. De novo protein crystal structure determination from X-ray free-electron laser data. Nature. 2014;505:244–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P41 RR012408/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM102520/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM055302/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- Y1GM008003/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM041574/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NIH 5R37 GM041574-26/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM095887/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103473/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM110501/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 GM055302/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NIH F32 GM097779-03/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM110501/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S06 GM008003/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM097779/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM041574/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM066569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41GM103393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 2-P41-RR012408/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM111244/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- 8P41GM103473-16/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM102520/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM095887/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NIH 5R01 GM066569-11/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM055302/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

