The Effect of Sustained Inflammation on Hepatic Mevalonate Pathway Results in Hyperglycemia
- PMID: 26997483
- PMCID: PMC4826308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.023
The Effect of Sustained Inflammation on Hepatic Mevalonate Pathway Results in Hyperglycemia
Abstract
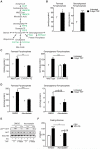
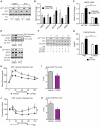
Control of plasma glucose level is essential to organismal survival. Sustained inflammation has been implicated in control of glucose homeostasis in cases of infection, obesity, and type 2 diabetes; however, the precise role of inflammation in these complex disease states remains poorly understood. Here, we find that sustained inflammation results in elevated plasma glucose due to increased hepatic glucose production. We find that sustained inflammation suppresses CYP7A1, leading to accumulation of intermediate metabolites at the branch point of the mevalonate pathway. This results in prenylation of RHOC, which is concomitantly induced by inflammatory cytokines. Subsequent activation of RHO-associated protein kinase results in elevated plasma glucose. These findings uncover an unexpected mechanism by which sustained inflammation alters glucose homeostasis.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
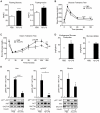
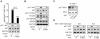
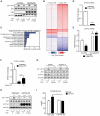
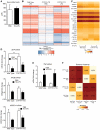

Comment in
-
Insulin Signaling in a Bit of a Jam.Cell. 2016 Apr 7;165(2):264-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.03.012. Cell. 2016. PMID: 27058657
References
-
- Alon U. Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:450–461. - PubMed
-
- Andrews RC, Walker BR. Glucocorticoids and insulin resistance: old hormones, new targets. Clin Sci. 1999;96:513–523. - PubMed
-
- Arkan MC, Hevener AL, Greten FR, Maeda S, Li Z-W, Long JM, Wynshaw-Boris A, Poli G, Olefsky J, Karin M. IKK-beta links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2005;11:191–198. - PubMed
-
- Barbour LA, McCurdy CE, Hernandez TL, Kirwan JP, Catalano PM, Friedman JE. Cellular Mechanisms for Insulin Resistance in Normal Pregnancy and Gestational Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:S112–S119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI089771/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI089771/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 2T32GM7205-36/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI055502/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA157461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI046688/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007205/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1F30DK094480/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI046688/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA157461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 DK094480/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R37 AI046688/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK059635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

